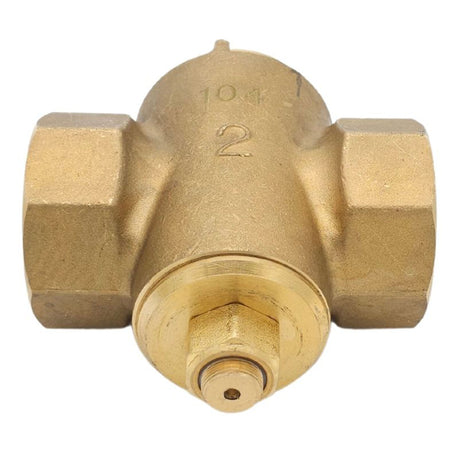
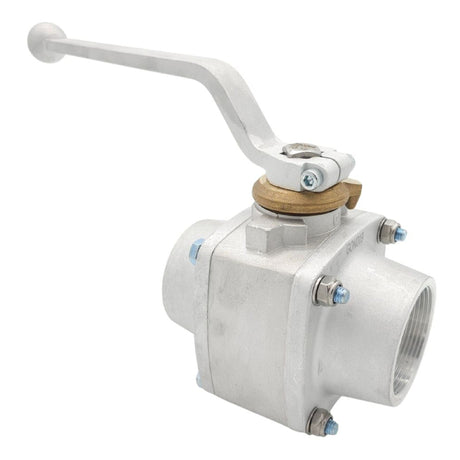
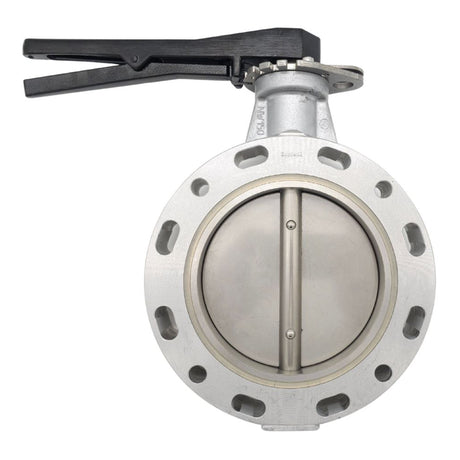
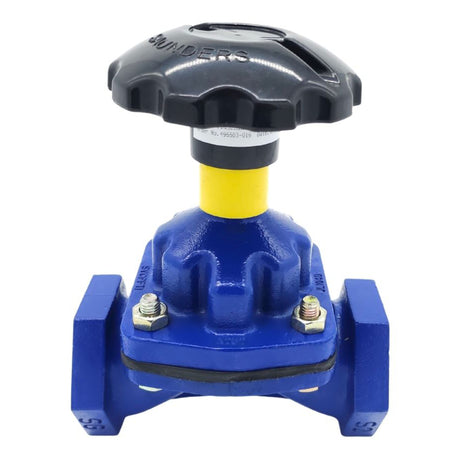
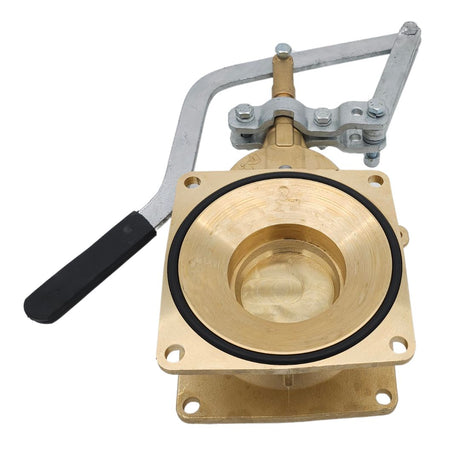
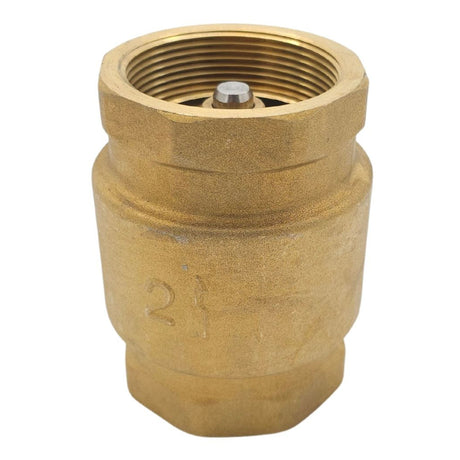
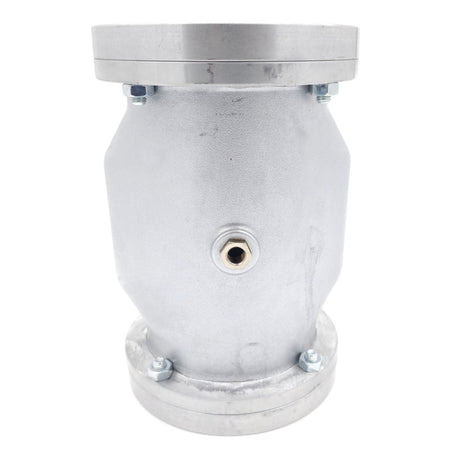
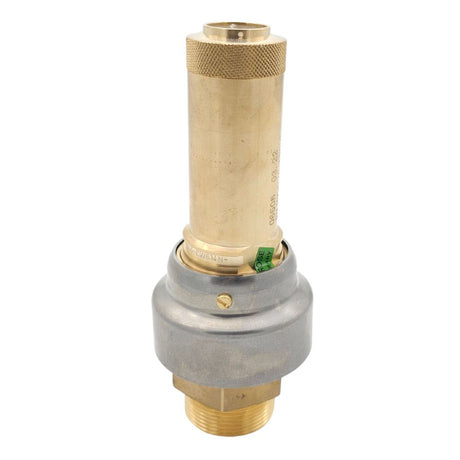
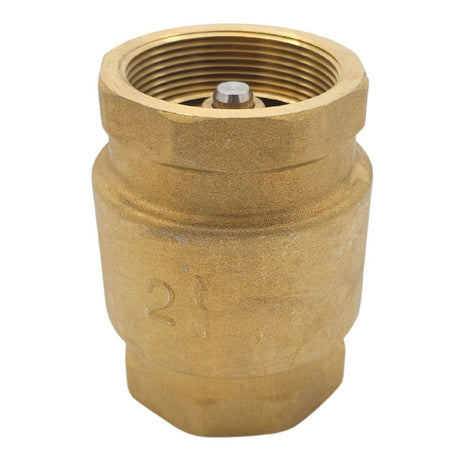
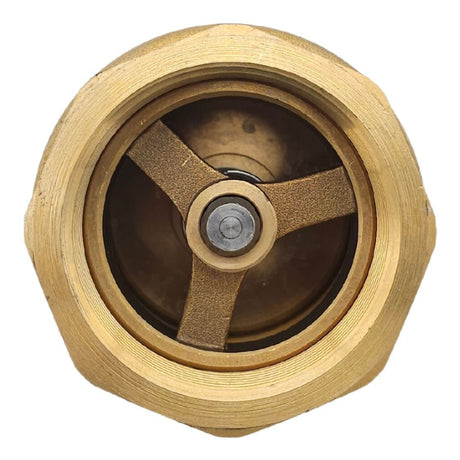
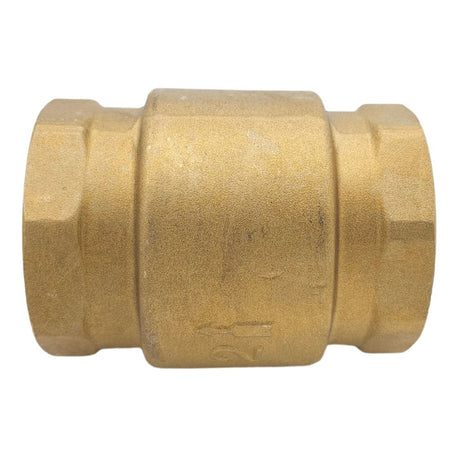
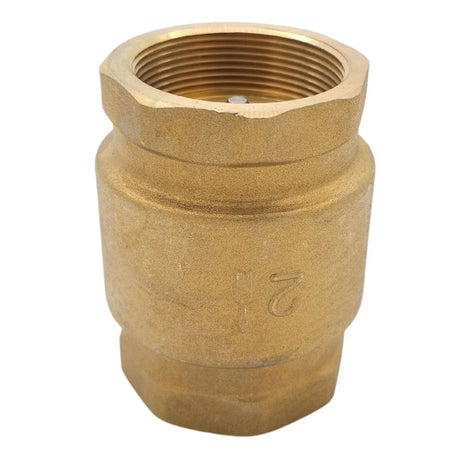
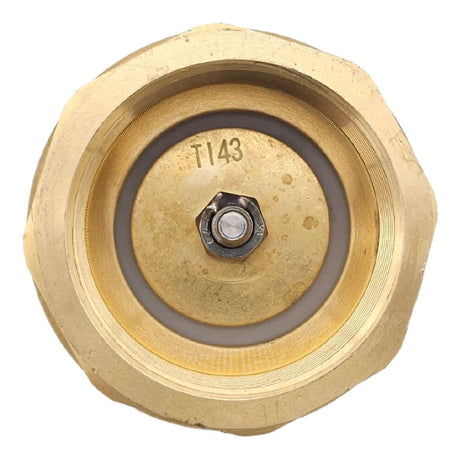
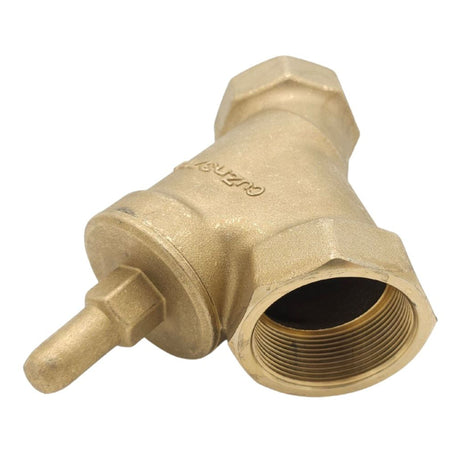
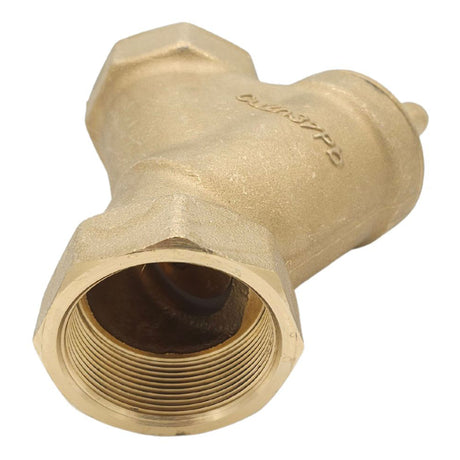
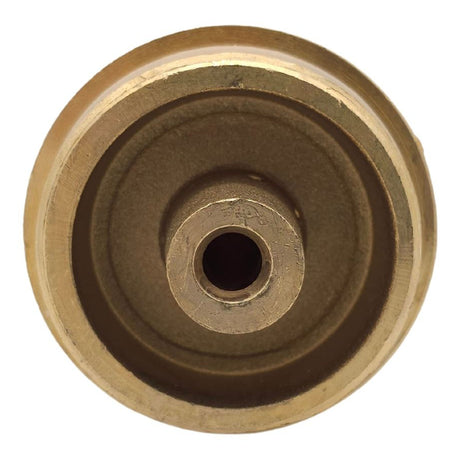
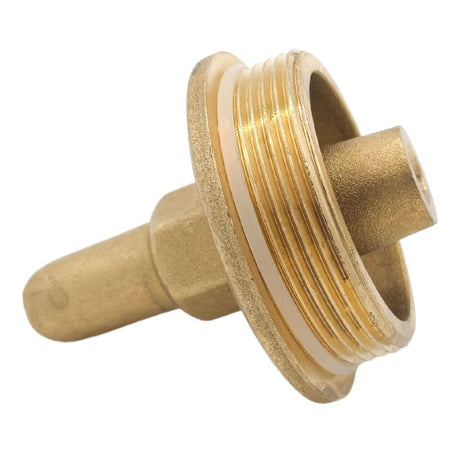
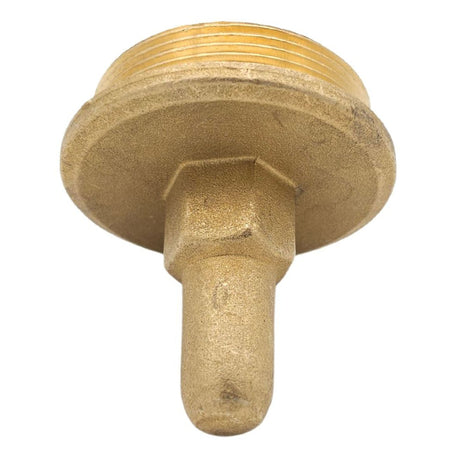
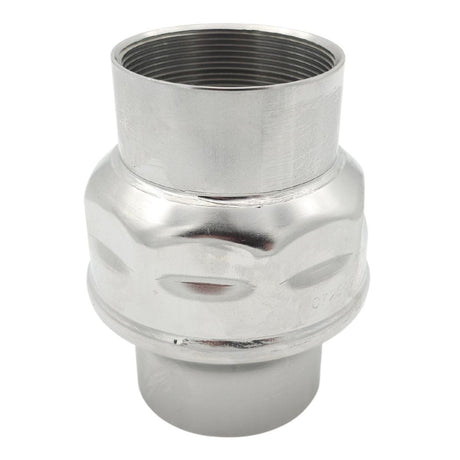
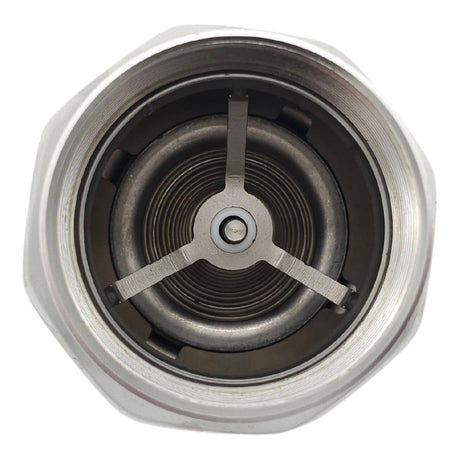
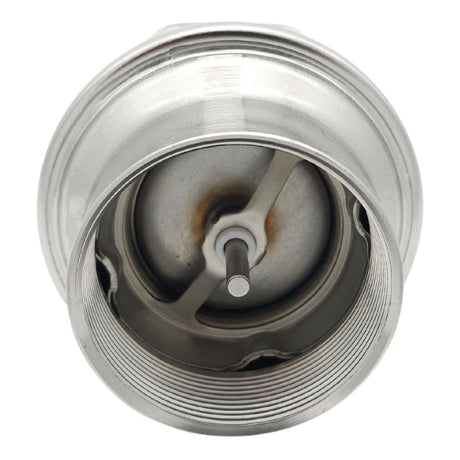
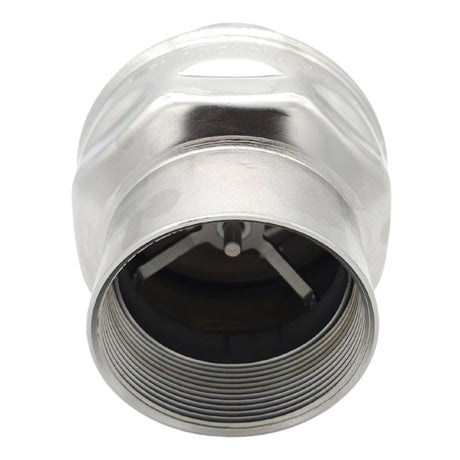
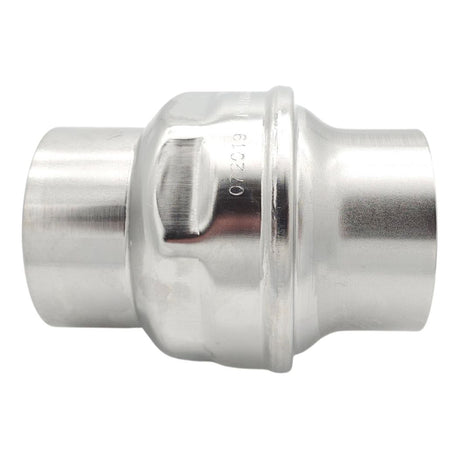
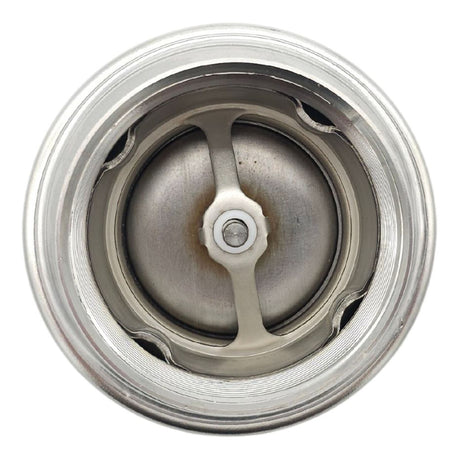
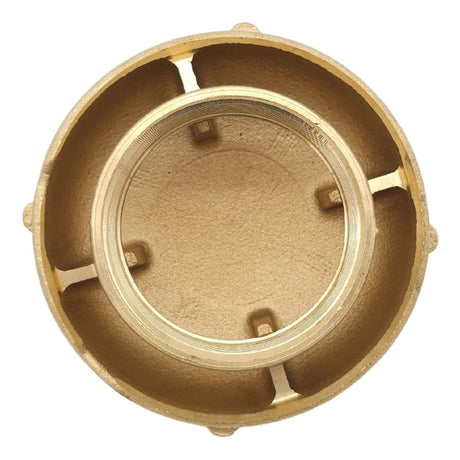
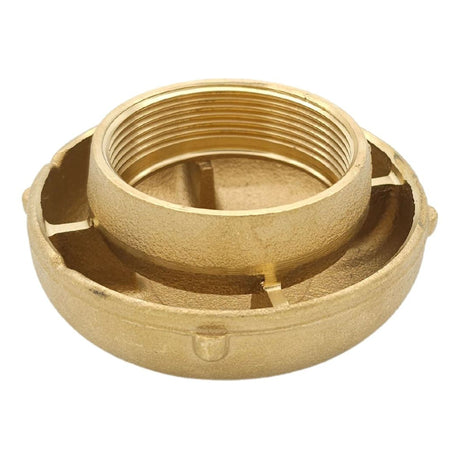
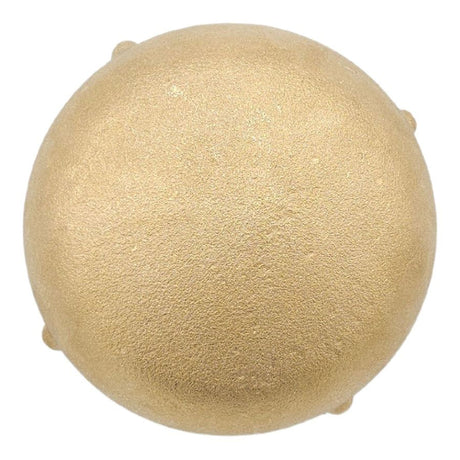
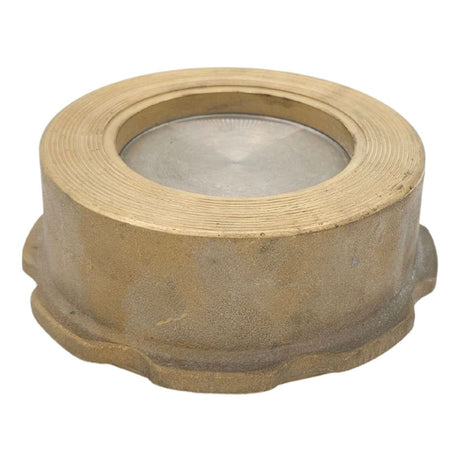
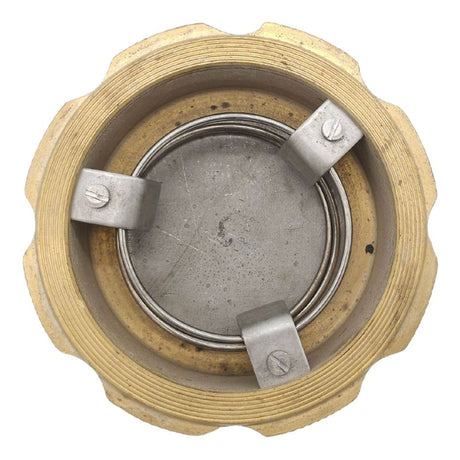
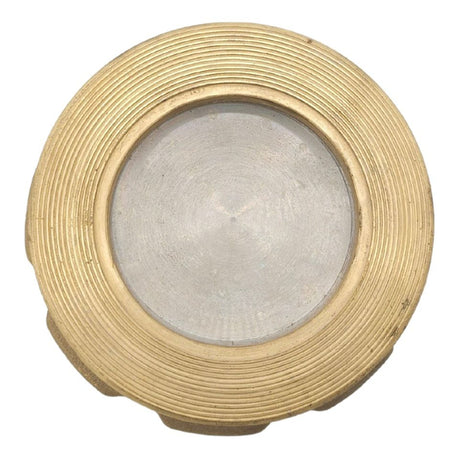
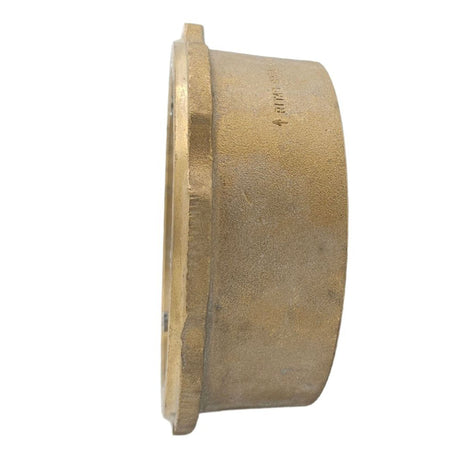
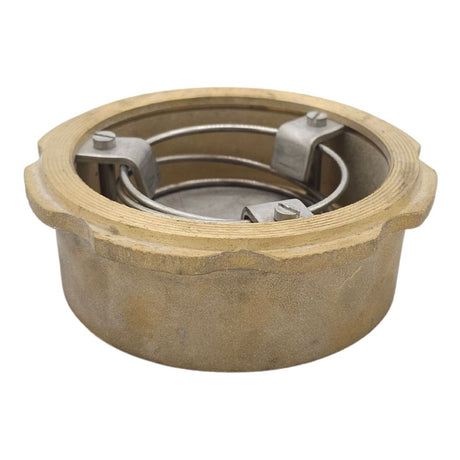
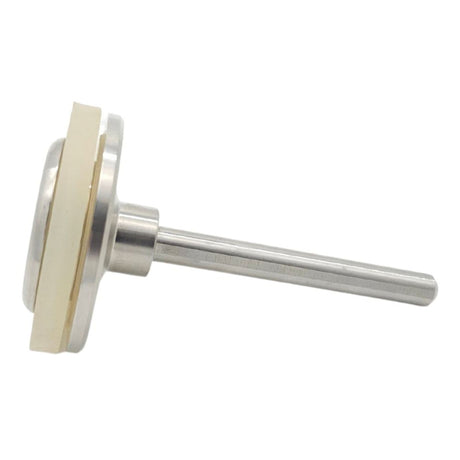
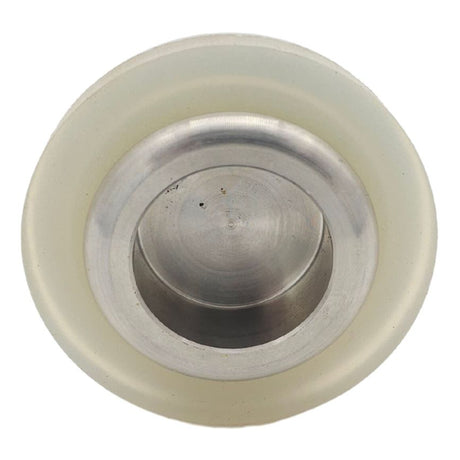
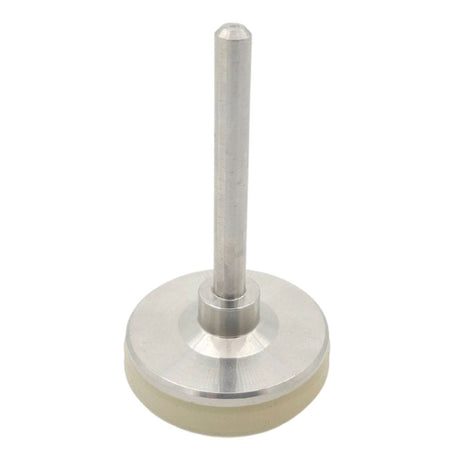
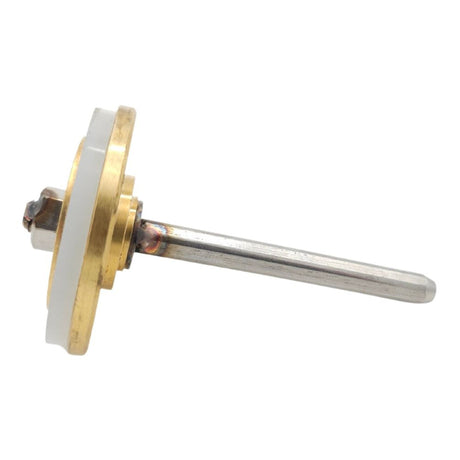
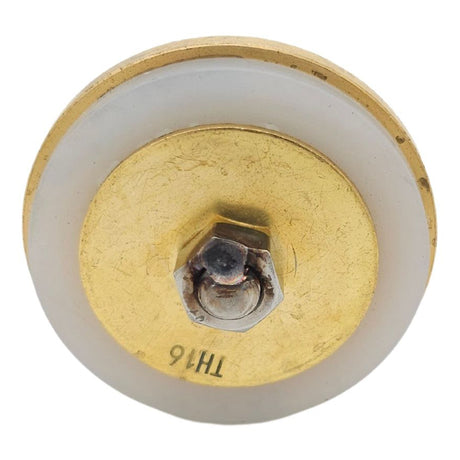
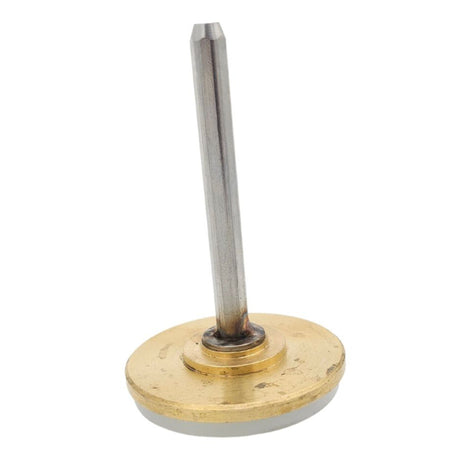
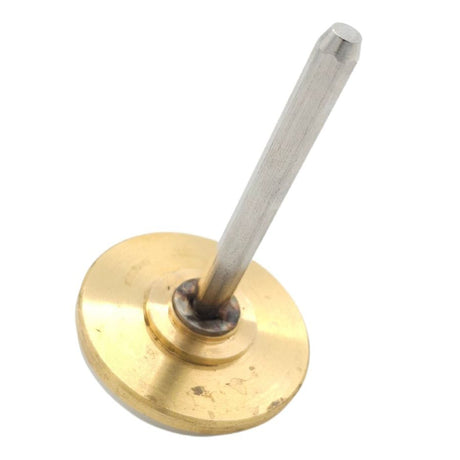
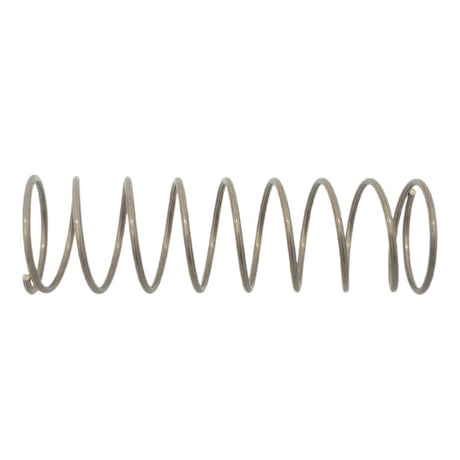
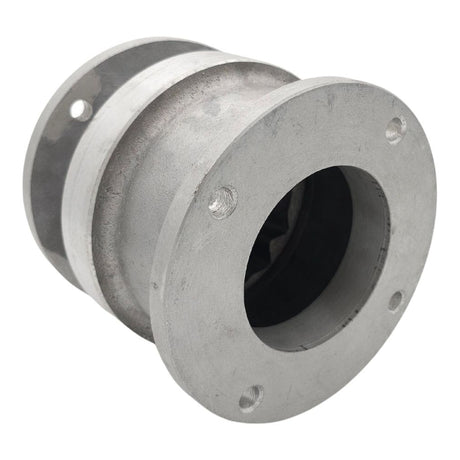
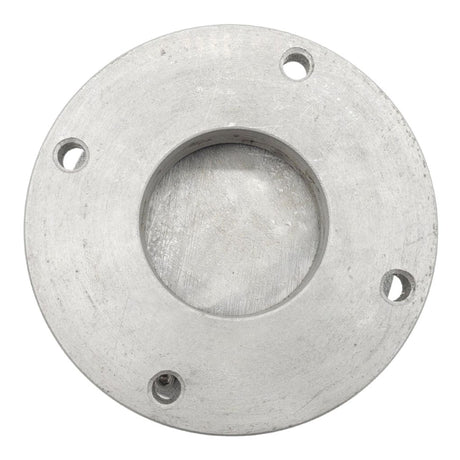
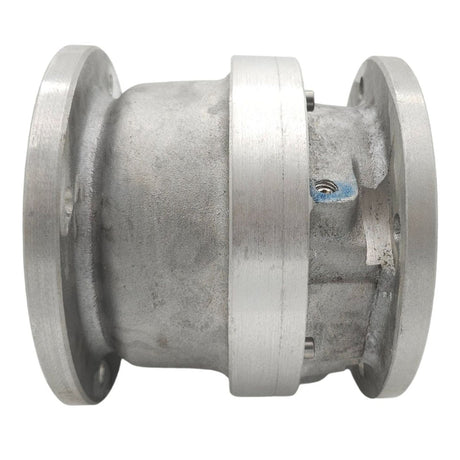
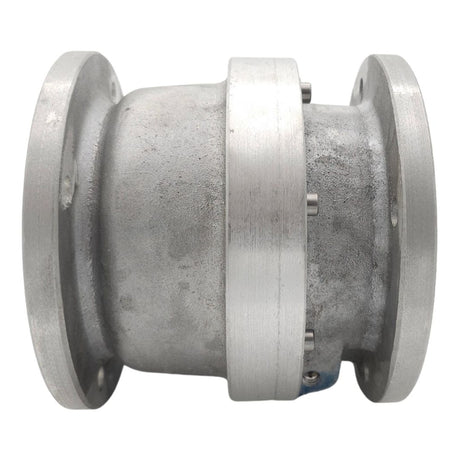
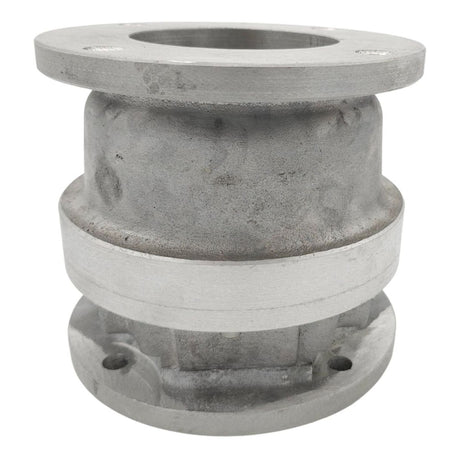
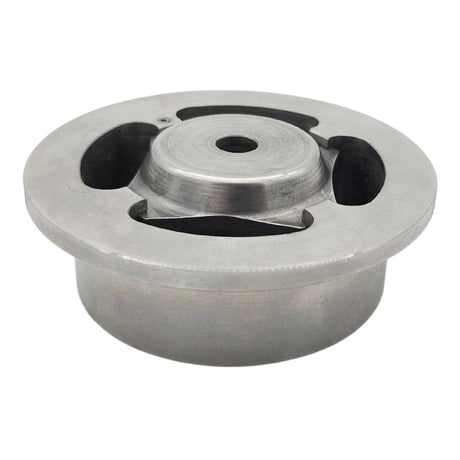
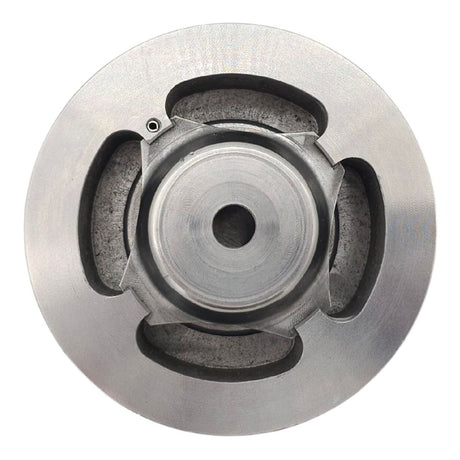
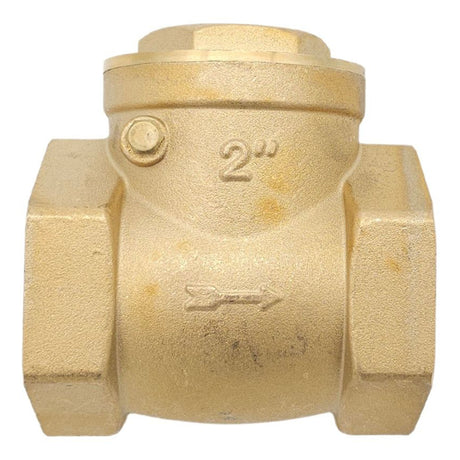
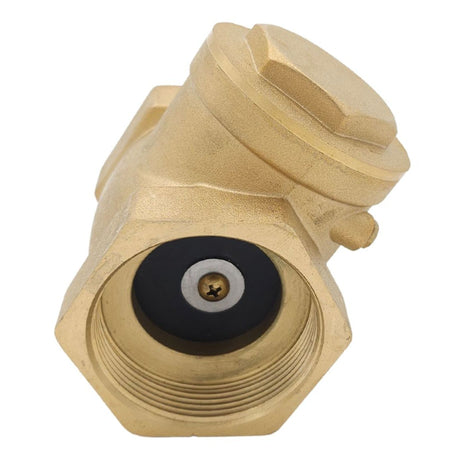
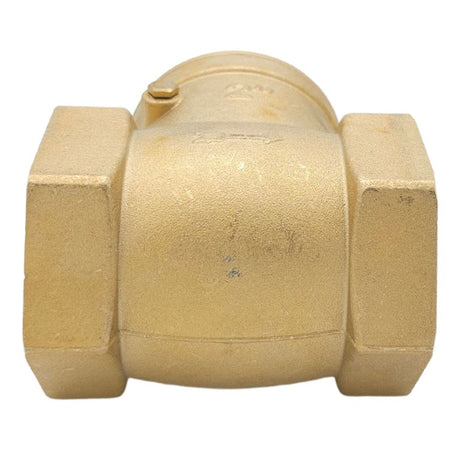
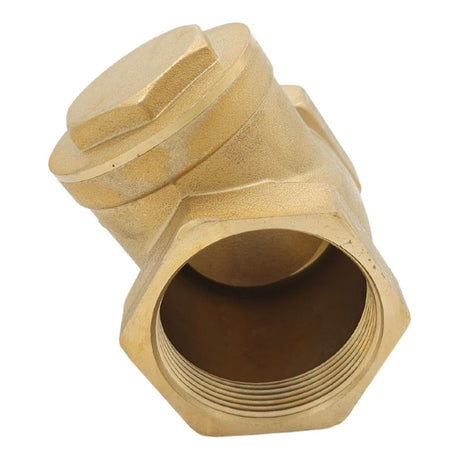
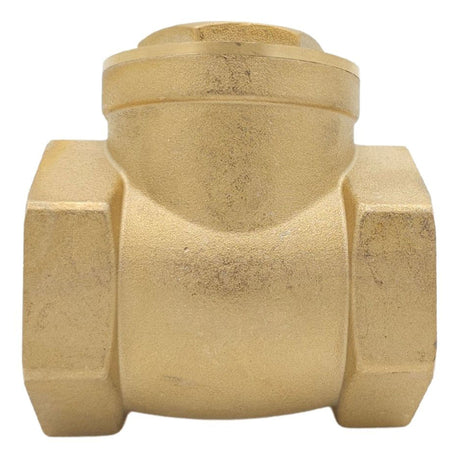
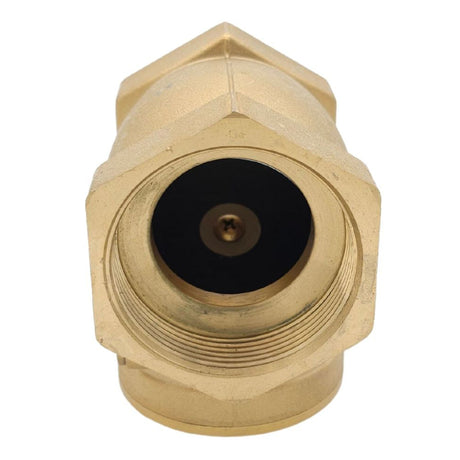
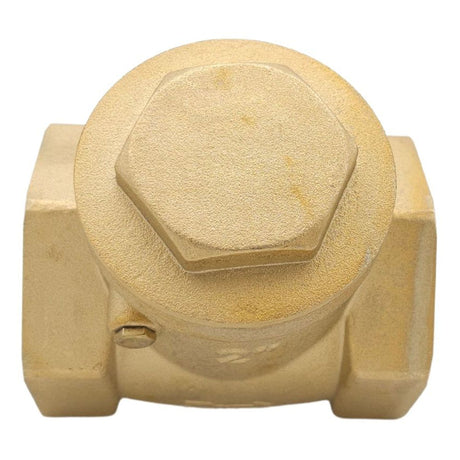
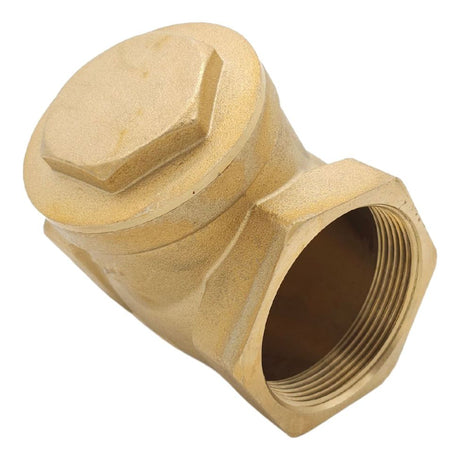
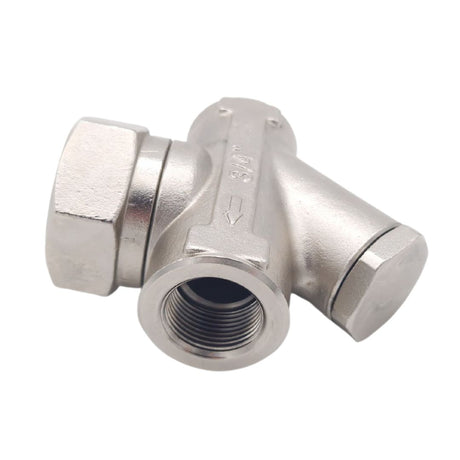
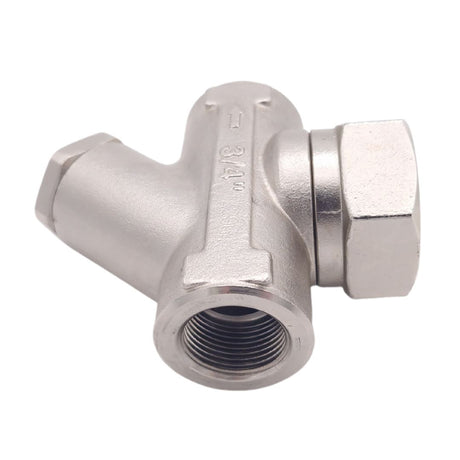
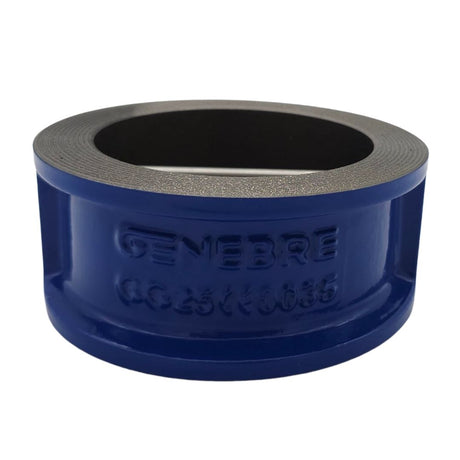
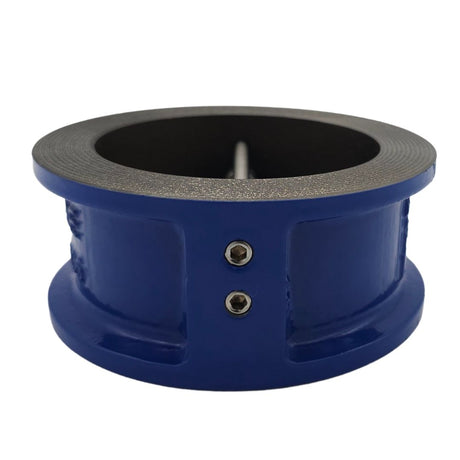
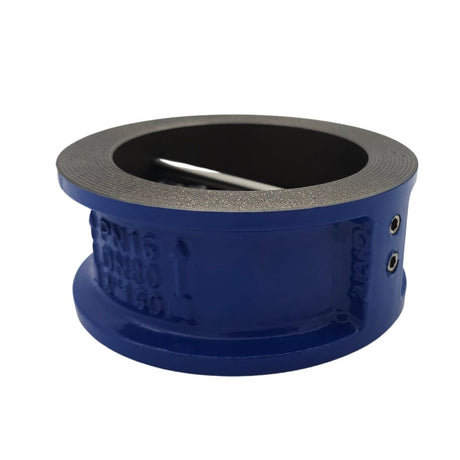
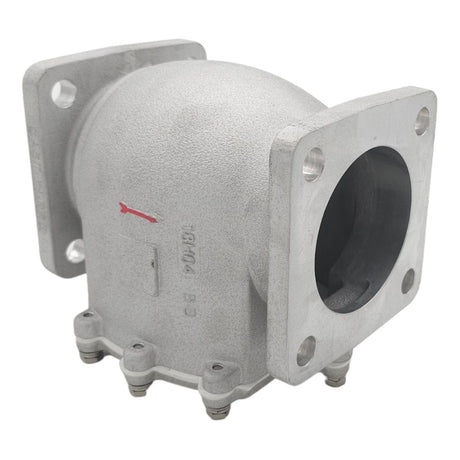
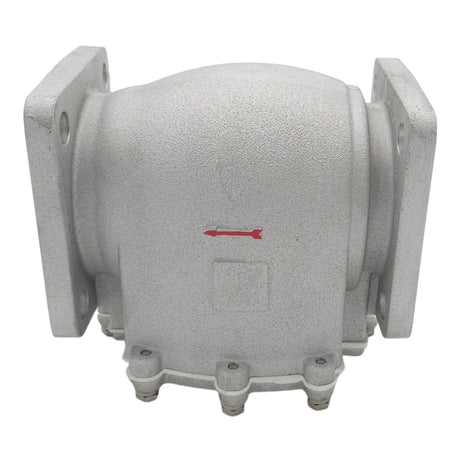
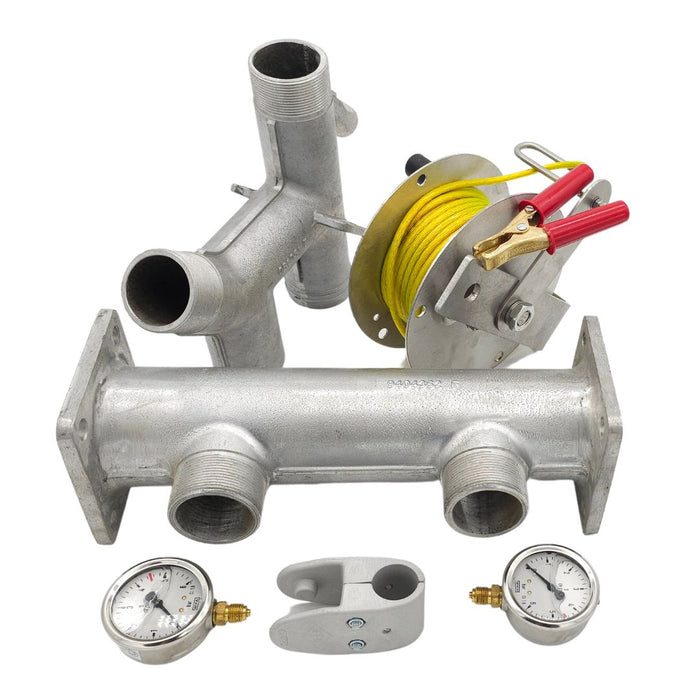
Europa Non Return Valve (Brass)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /Unavailable- Regular price £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
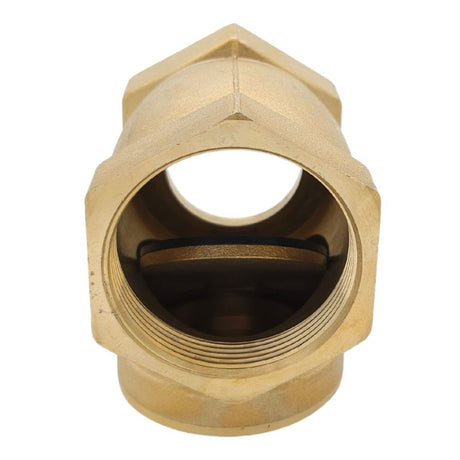
Brass Angle Non Return Valve Cap
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableMondeo Non Return Valve (Stainless Steel)
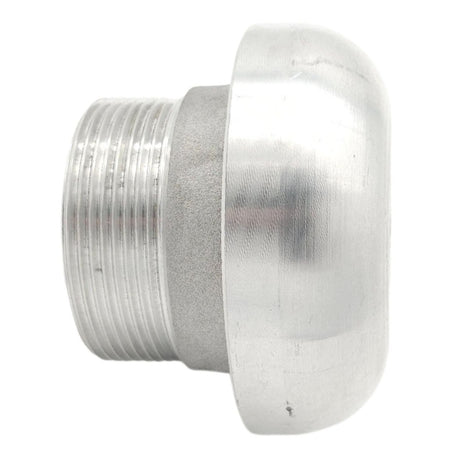
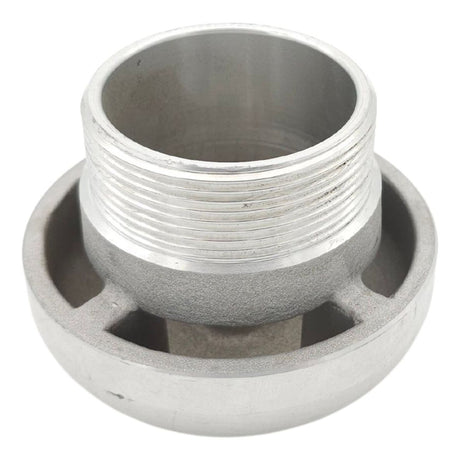
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableBreather Cap 2" BSP Male (Aluminium)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableFFB Breather Cap 2" BSP (Brass)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableRITAG Wafer Type Non Return Valve (Brass)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableBrass Angle Non Return Valve Plunger (Stainless Steel)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableBrass Angle Non Return Valve Plunger
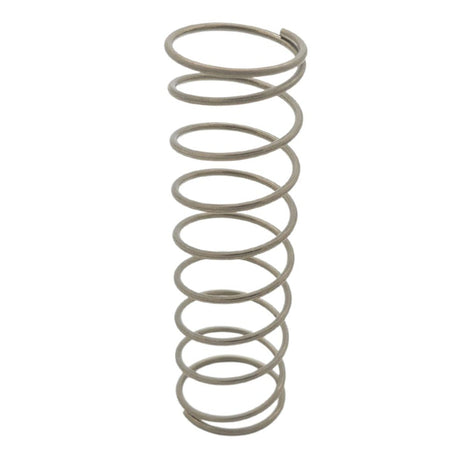
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableBrass Angle Non Return Valve Spring (2" - 3")
Regular price £0.01Unit price /Unavailable- Regular price £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
- Regular price £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
RITAG Non Return Valve Graphite Gasket 65mm Large (130 x 100 x 3mm)
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableBSP Swing Check Non Return Valve (Brass)
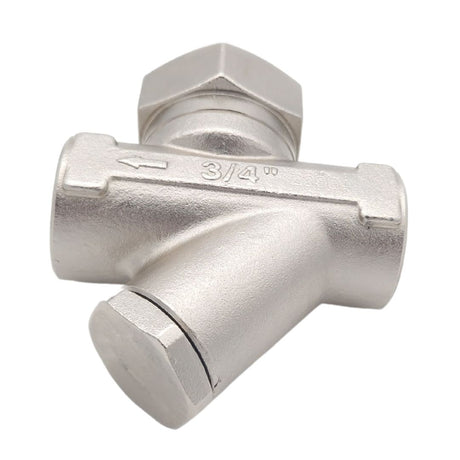
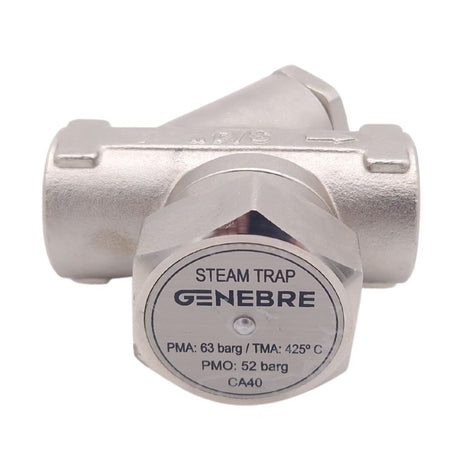
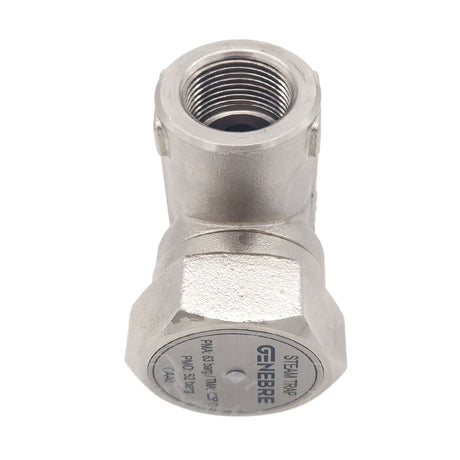
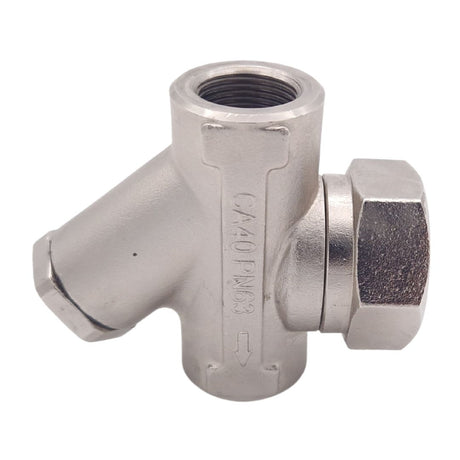
Regular price £0.01Unit price /UnavailableSteam Trap With Strainer BSP Threaded
Regular price £0.00Unit price /UnavailableMission Non Return Valve Dual Plate (Cast Iron)
Regular price £0.00Unit price /UnavailableSureseal Swing Check Non Return Valve
Regular price £0.00Unit price /UnavailableAngle Non Return Valve (Aluminium)
Regular price £0.00Unit price /Unavailable
Non-return valves, also known as check valves, are essential components in fluid systems designed to allow flow in one direction while preventing backflow. These valves are widely used in industries such as water management, oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, where maintaining unidirectional flow is critical for system efficiency and protection. Non-return valves help safeguard pumps, compressors, and other equipment from damage caused by reverse flow, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the entire system.
The key advantage of non-return valves lies in their self-acting design, which means they operate automatically based on the pressure and flow of the fluid. Common types of non-return valves include swing check valves, which use a hinged flap to control flow, lift check valves, where a disc lifts to allow flow and reseats to prevent backflow, and ball check valves, which utilize a ball to block reverse flow. These designs are chosen based on specific system requirements, such as pressure, flow rate, and the type of fluid being handled. Non-return valves are constructed from durable materials like stainless steel, brass, plastic, or cast iron to withstand various operational conditions.
Non-return valves are available in a variety of sizes and configurations, making them adaptable to different system setups. They are easy to install and require minimal maintenance, offering a cost-effective solution for enhancing system safety and performance. By preventing reverse flow, non-return valves protect equipment from potential damage, maintain pressure levels, and ensure the efficient operation of fluid systems. Whether used in pipelines, irrigation systems, or industrial processing plants, non-return valves are a dependable choice for professionals seeking reliable and efficient flow control solutions.Interested in a Quote?
Advantages of Using Non-Return Valves (Check Valves)
-
Prevents Backflow
-
Protects Equipment
-
Automatic Operation
-
Low Pressure Loss
-
Simple and Compact Design
-
Energy Efficiency