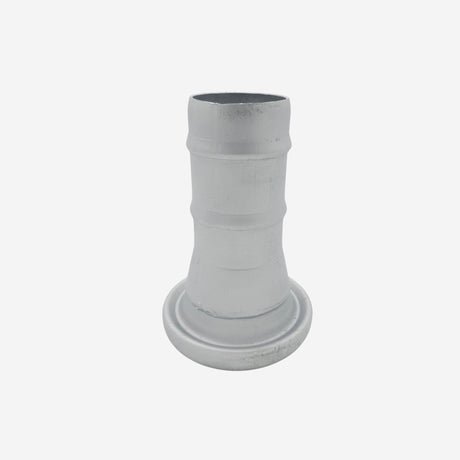
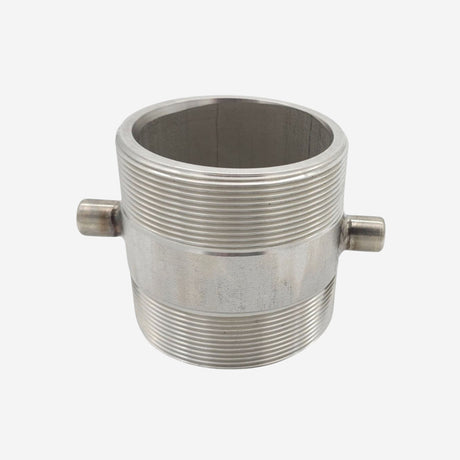
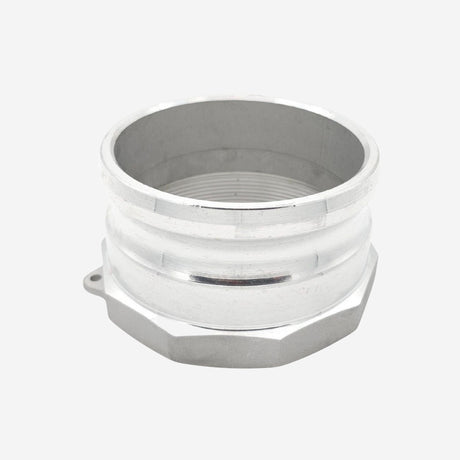
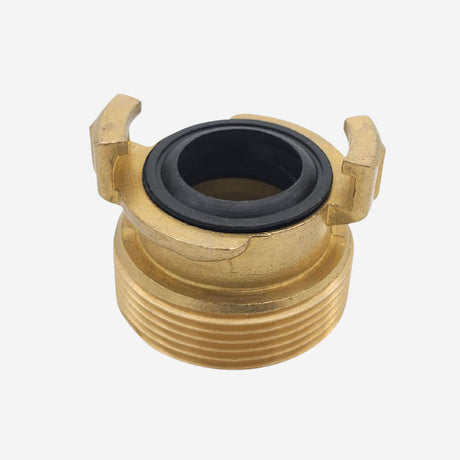
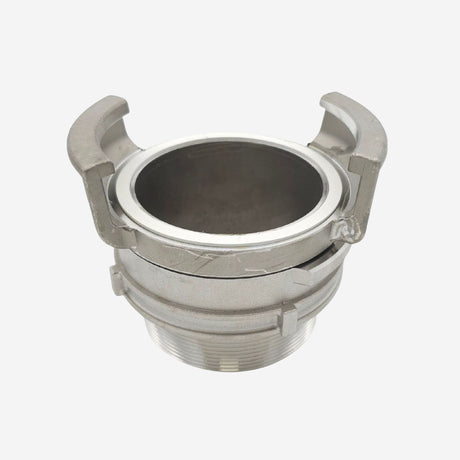
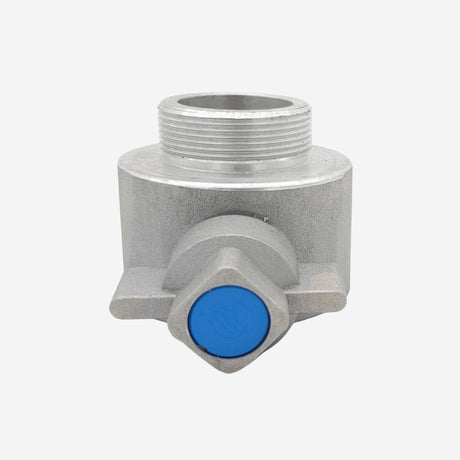
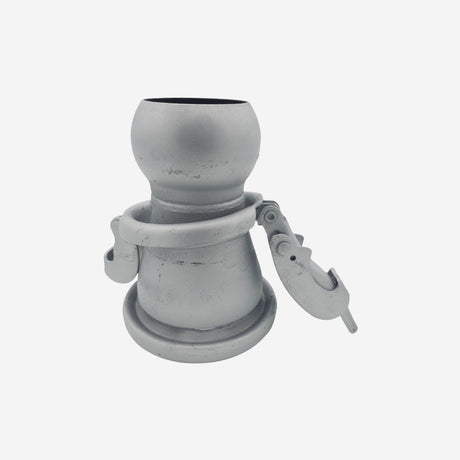
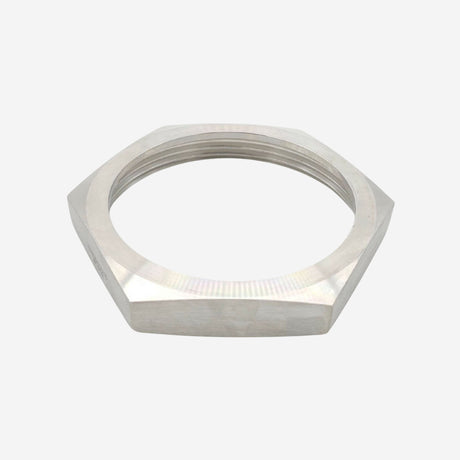
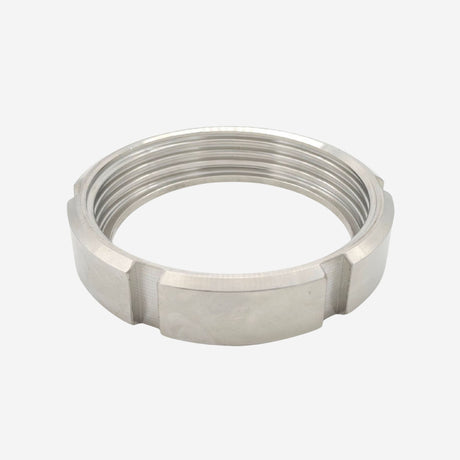
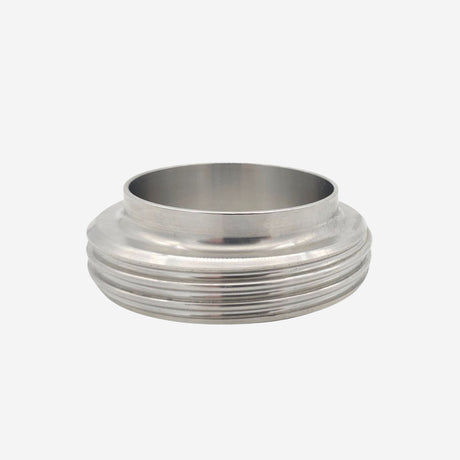
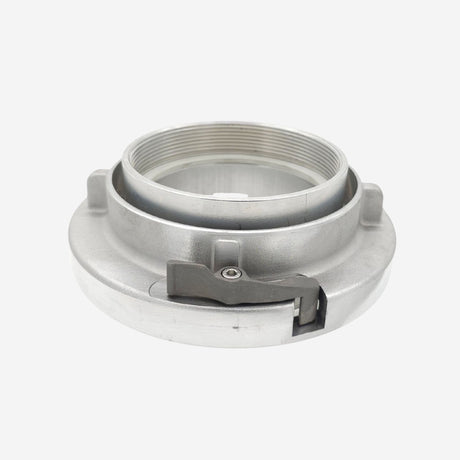
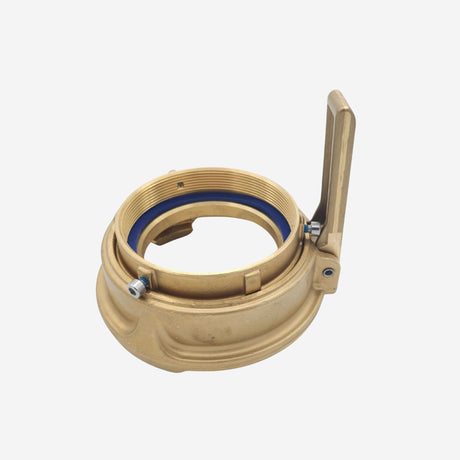
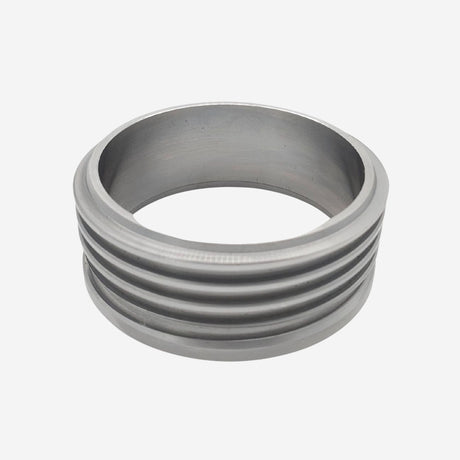
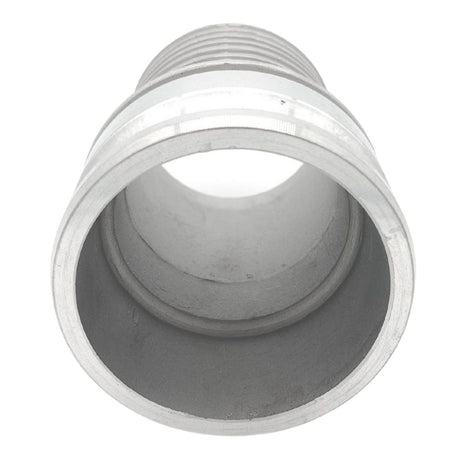
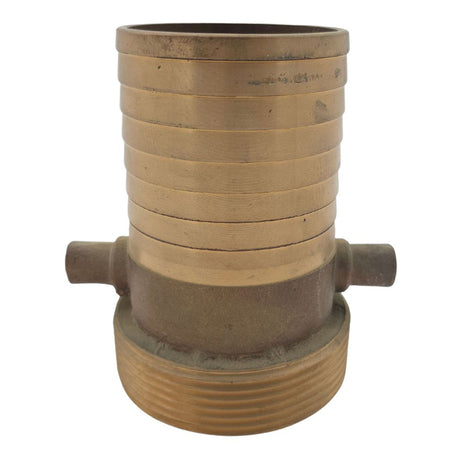
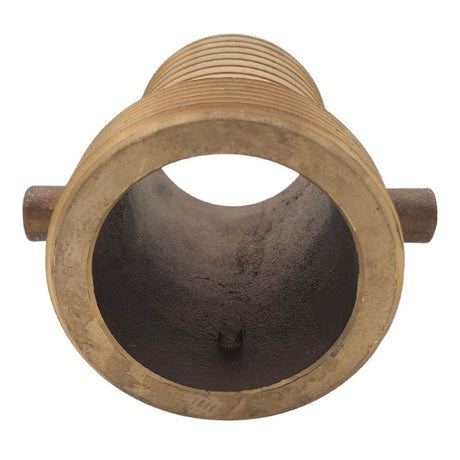
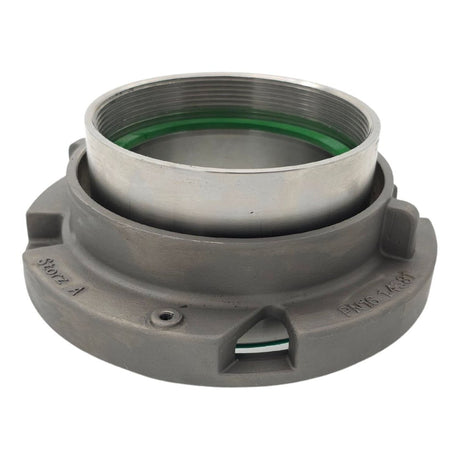
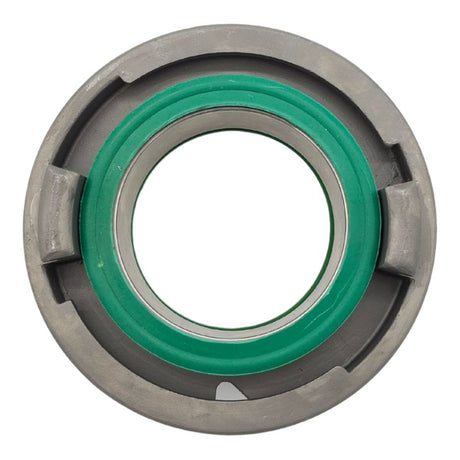
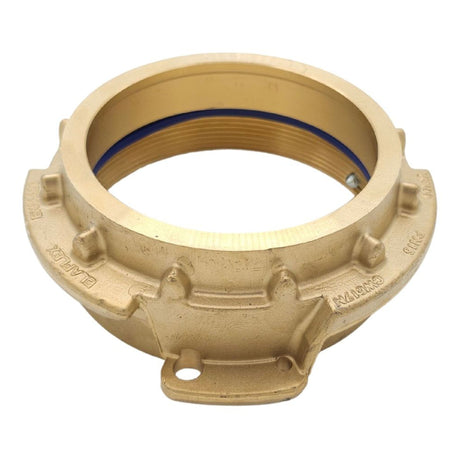
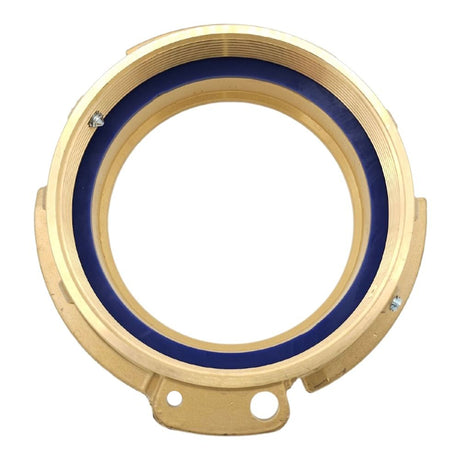
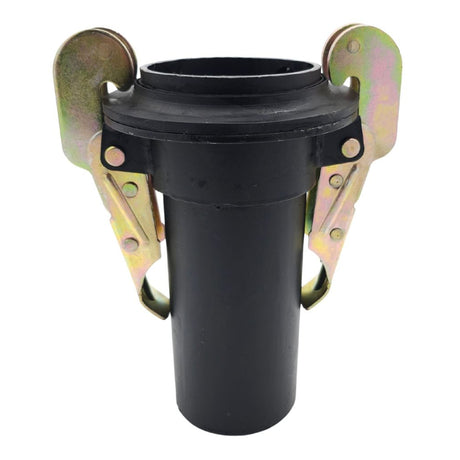
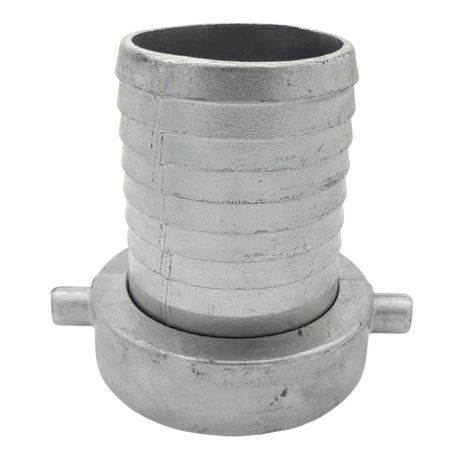
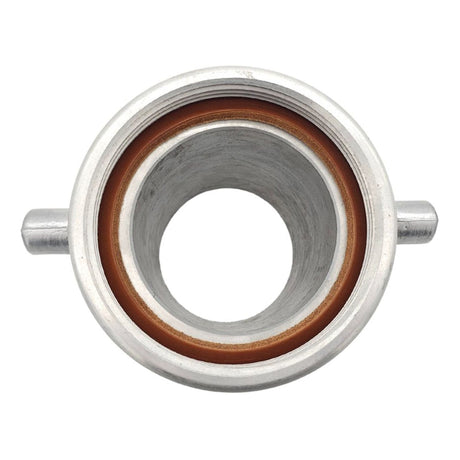
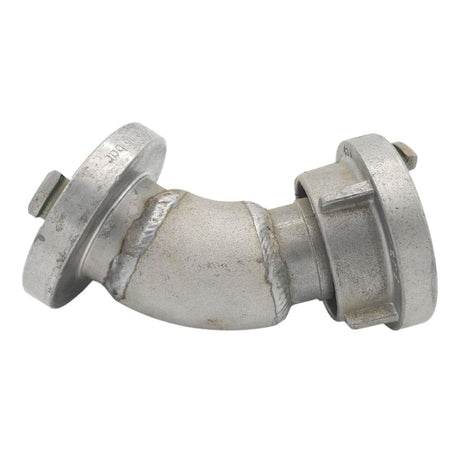
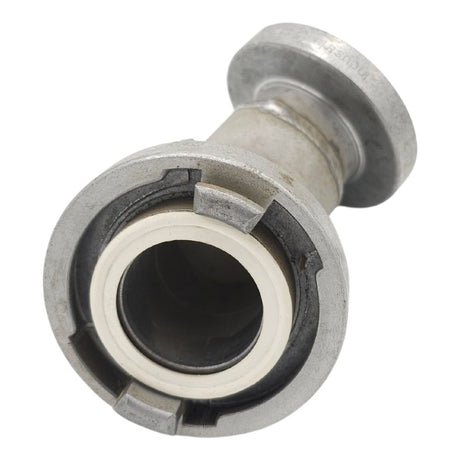
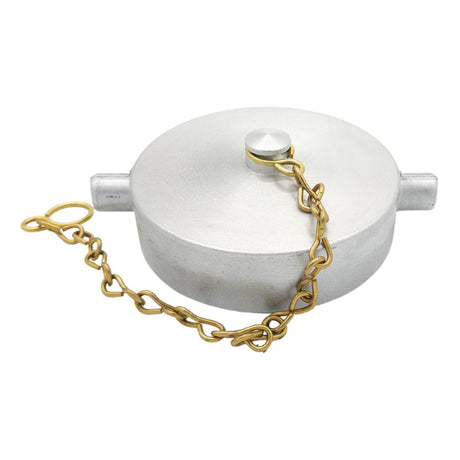
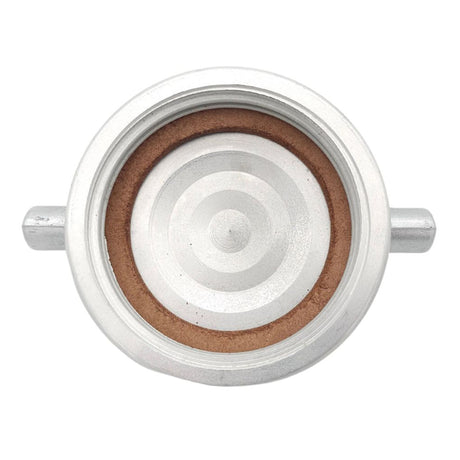
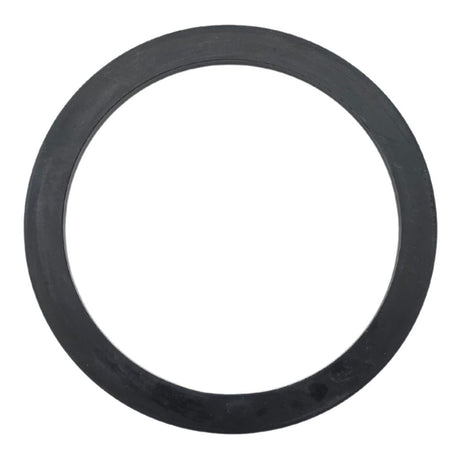
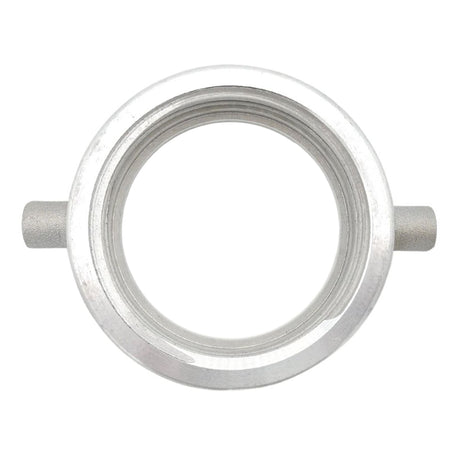
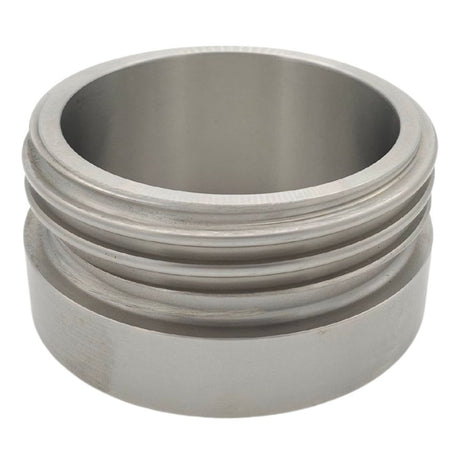
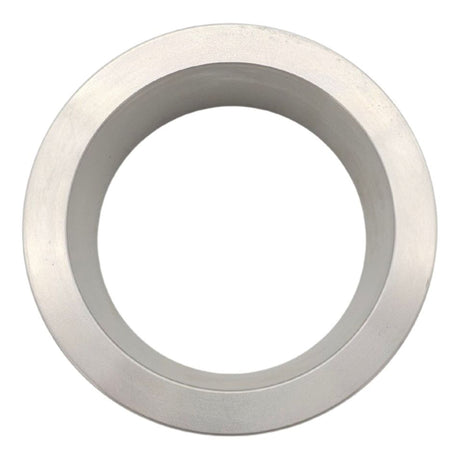
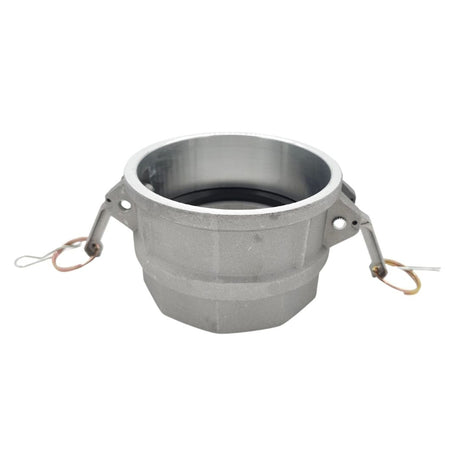
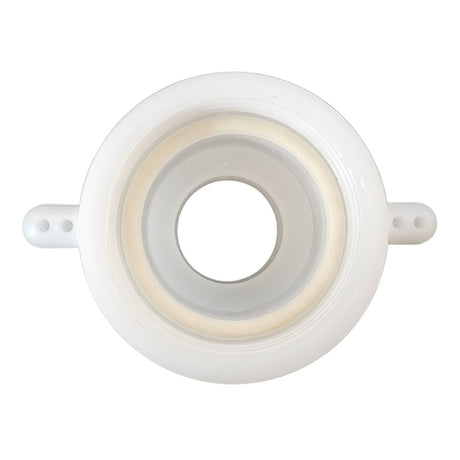
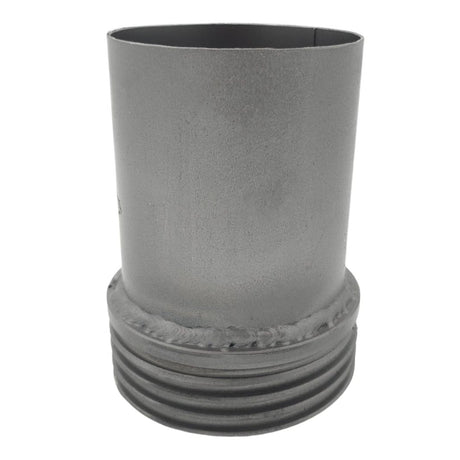
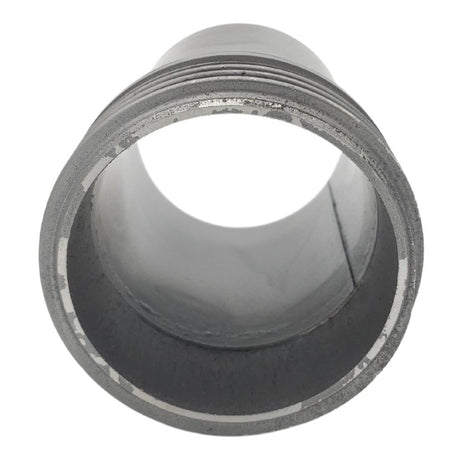
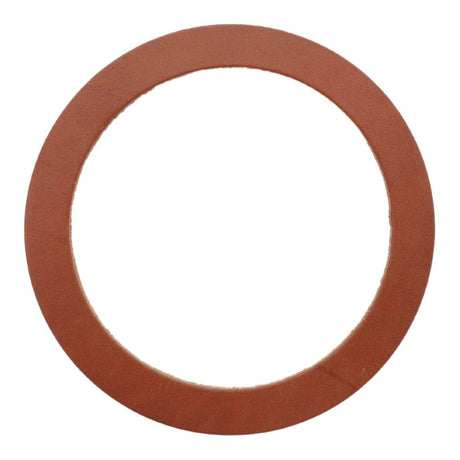
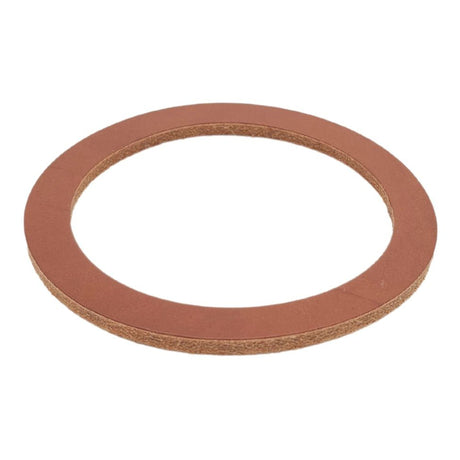
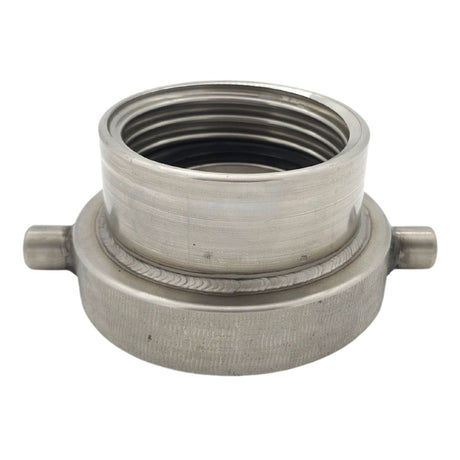
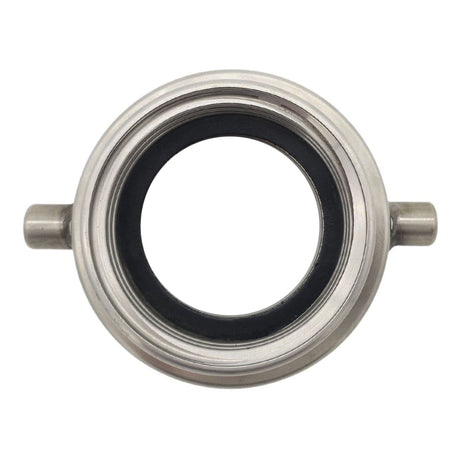
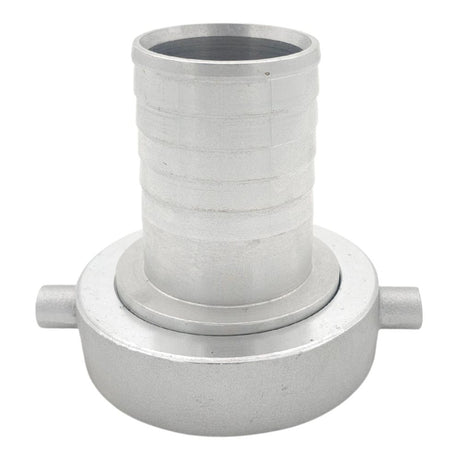
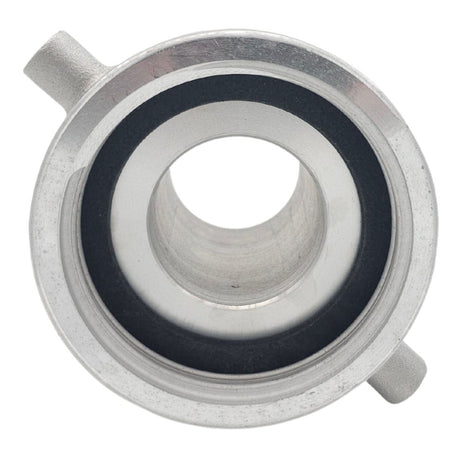
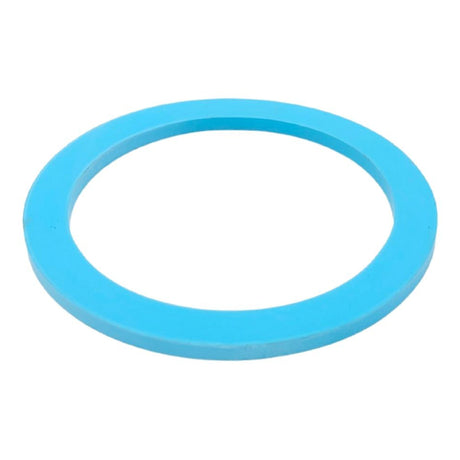
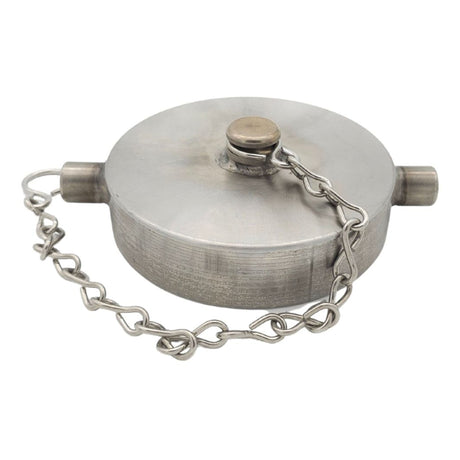
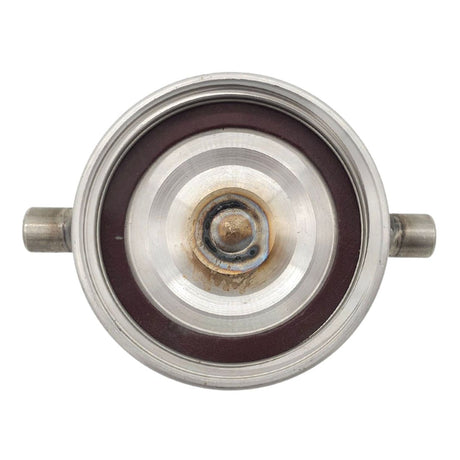
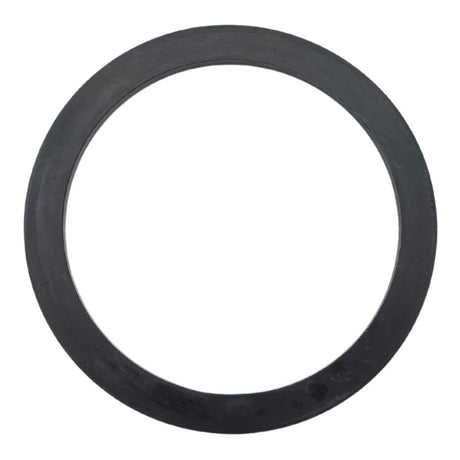
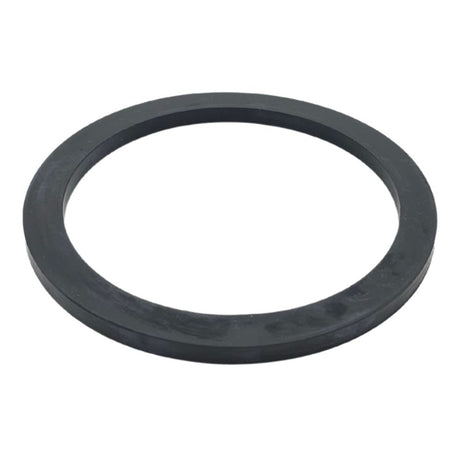
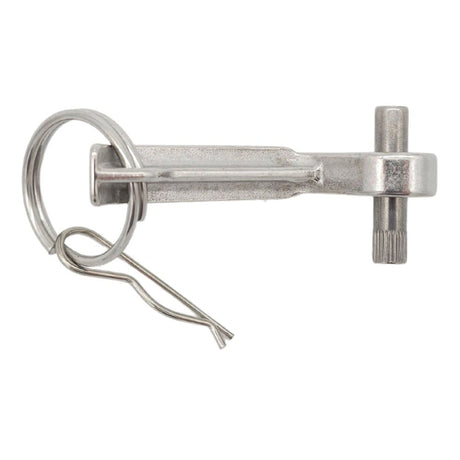
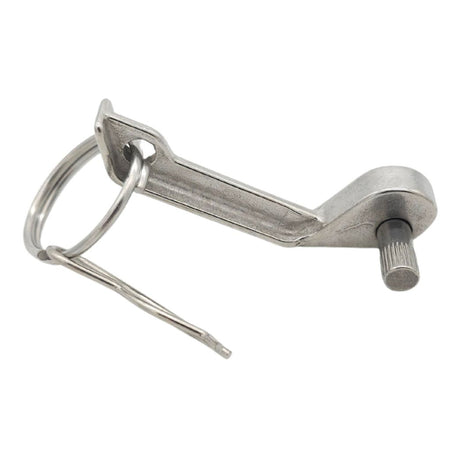
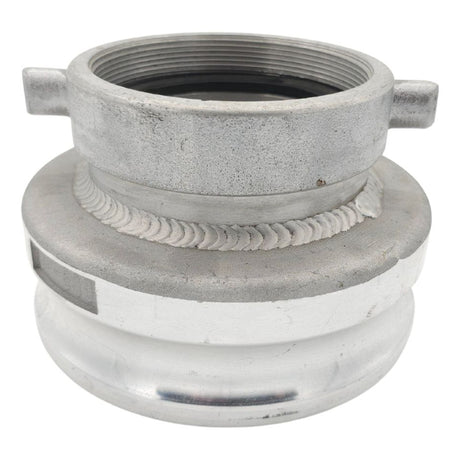
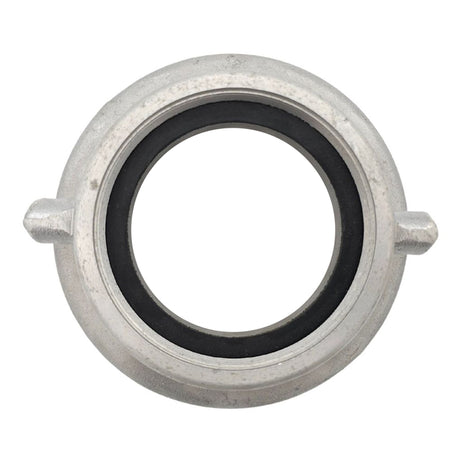
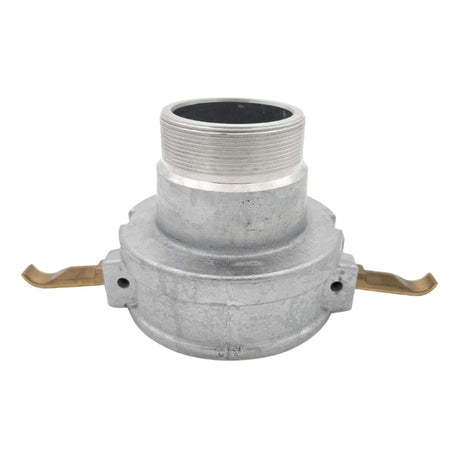
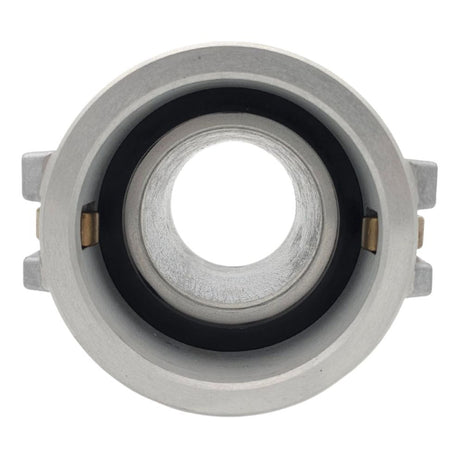
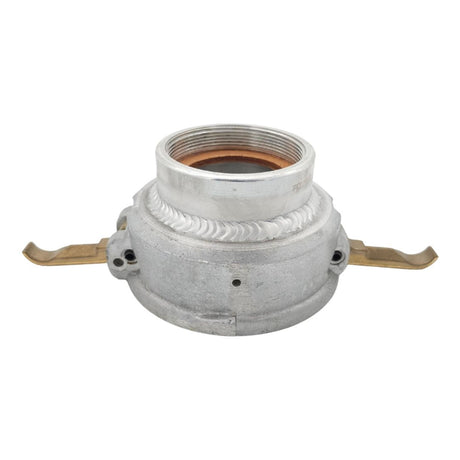
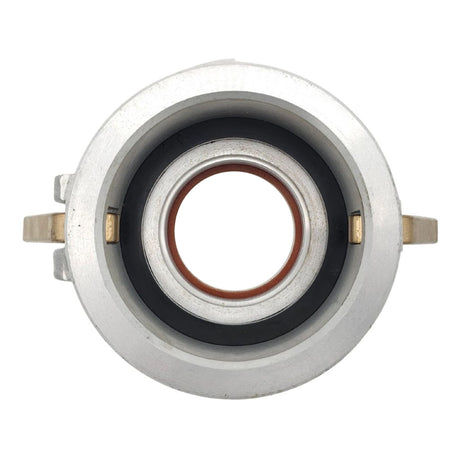
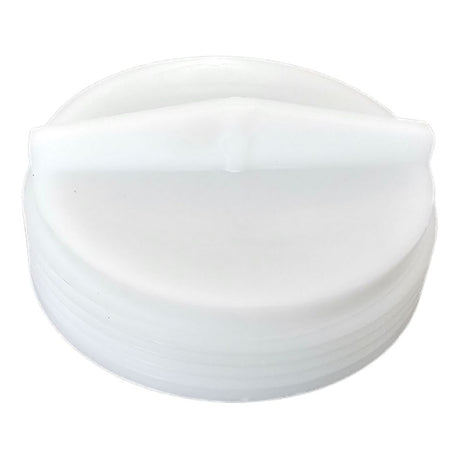
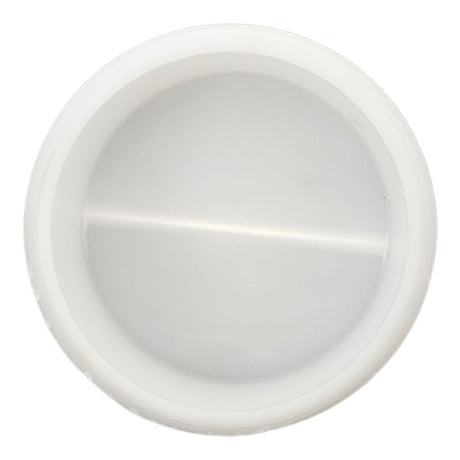
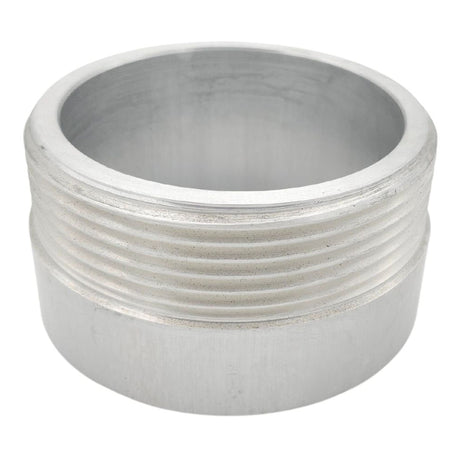
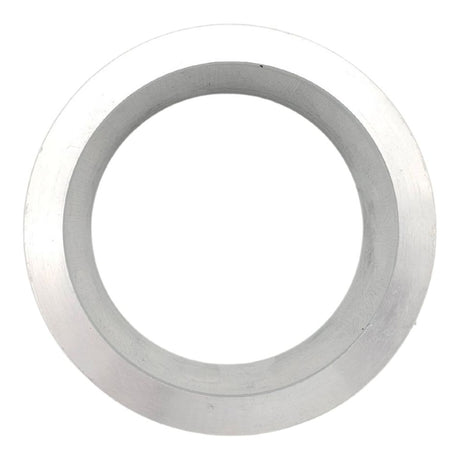
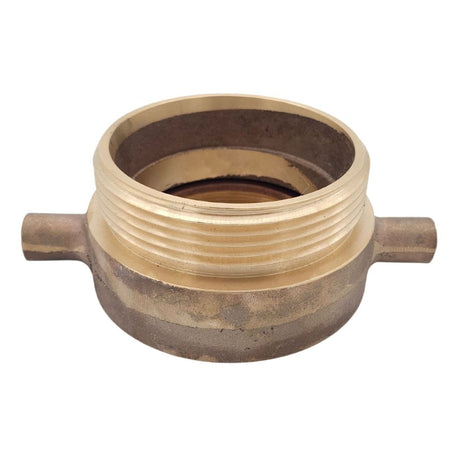
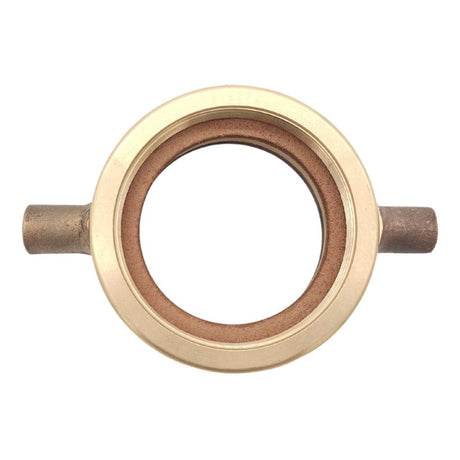
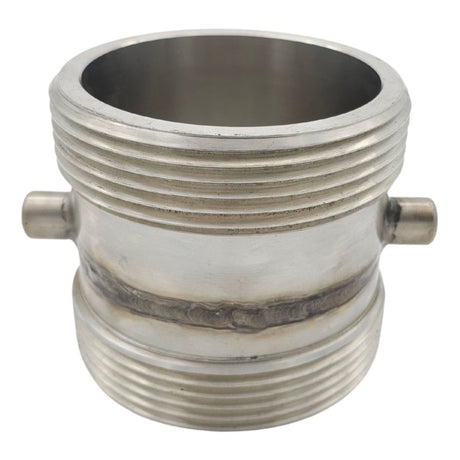
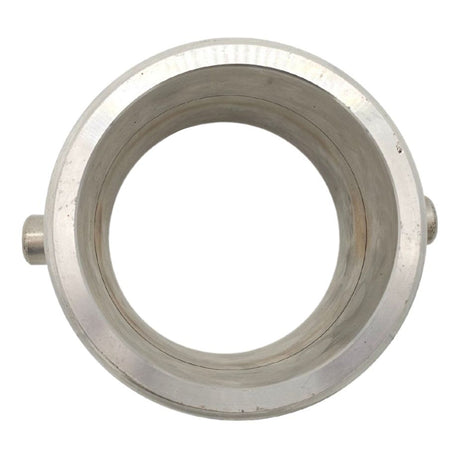
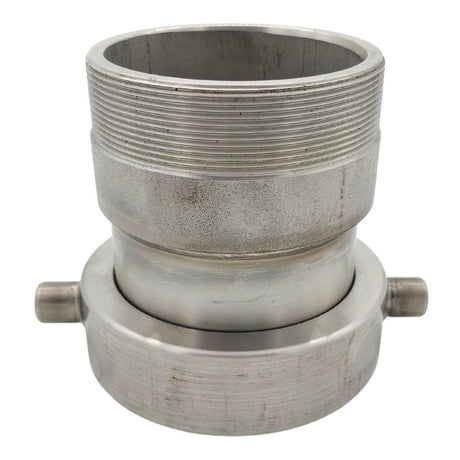
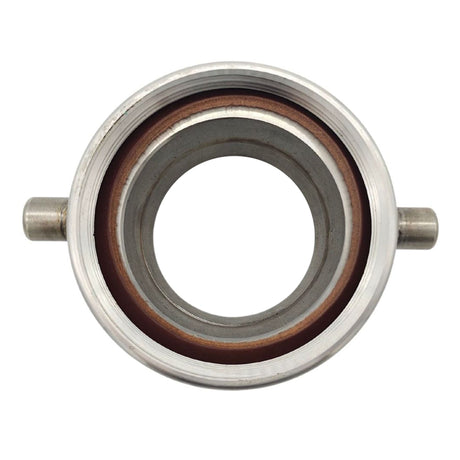
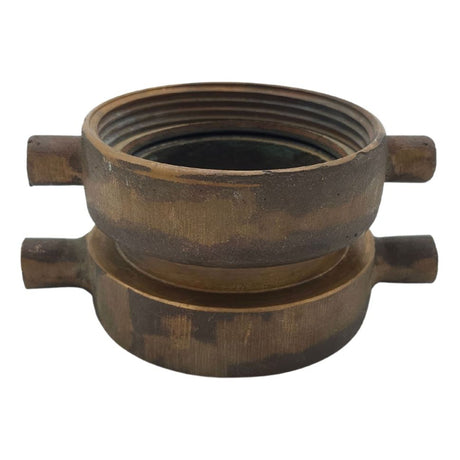
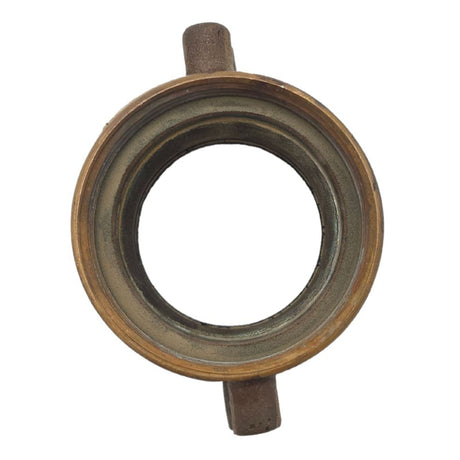
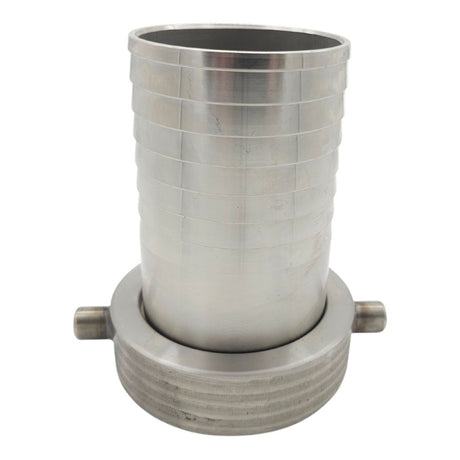
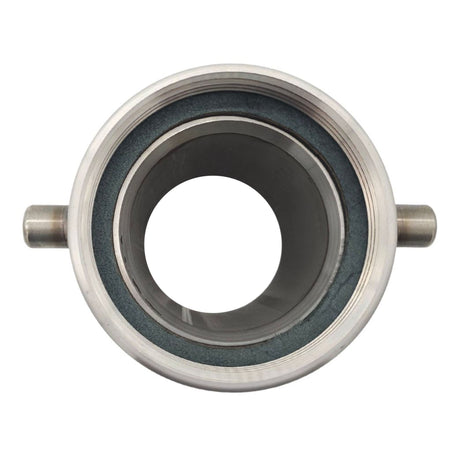
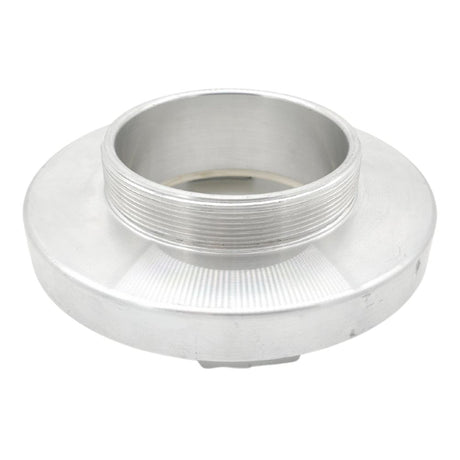
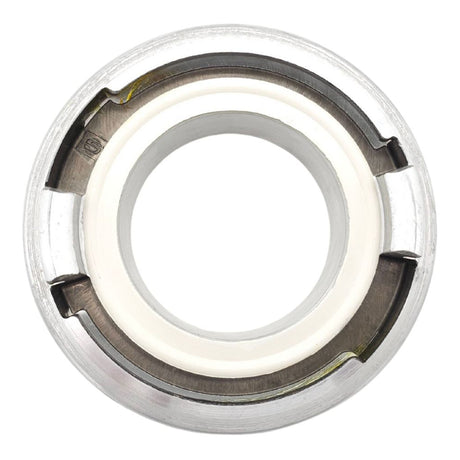
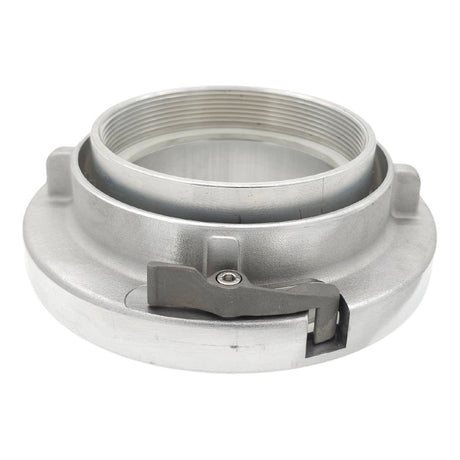
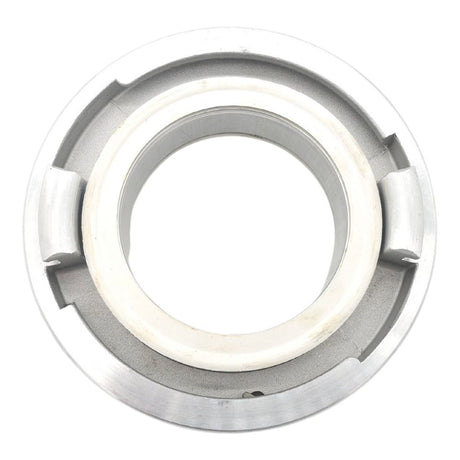
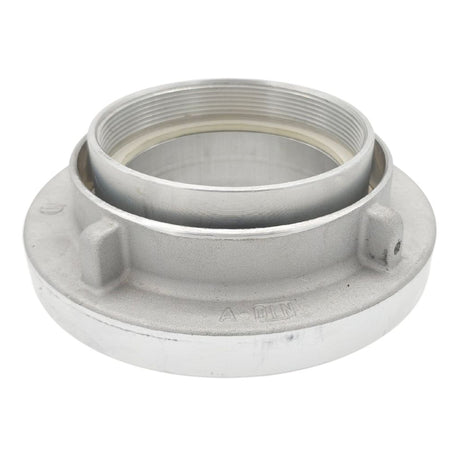
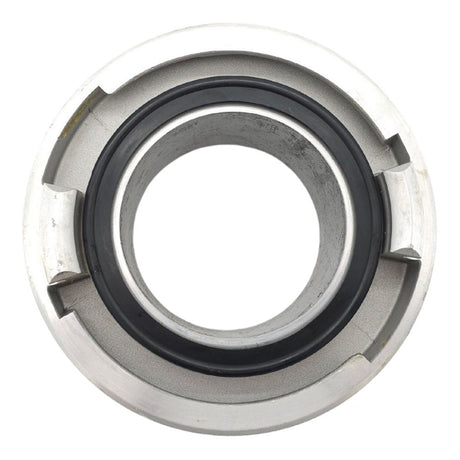
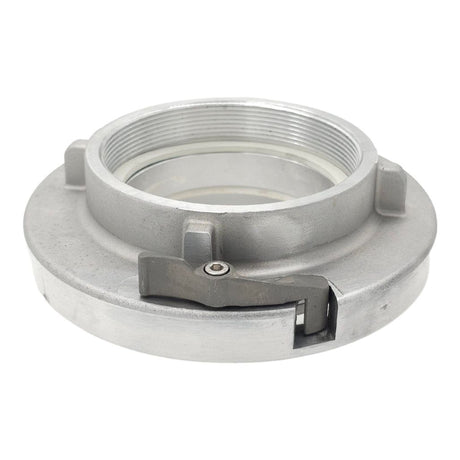
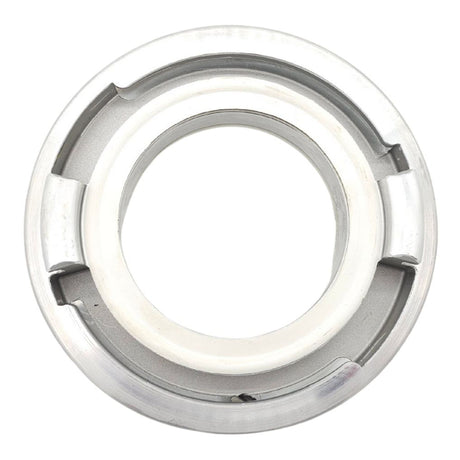
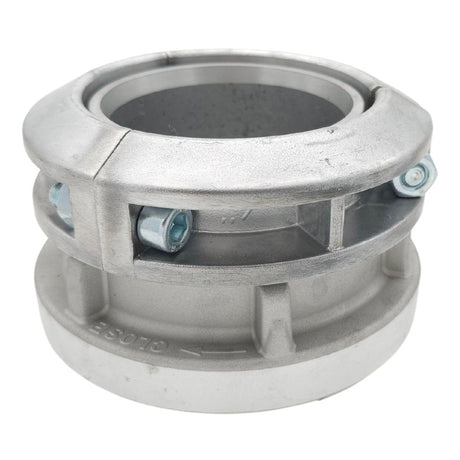
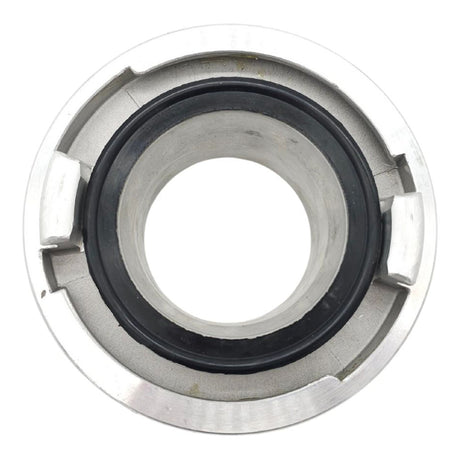
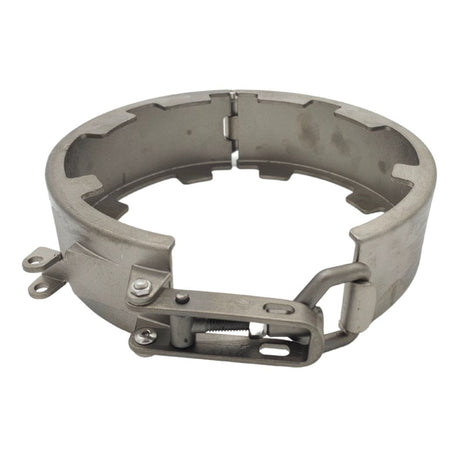
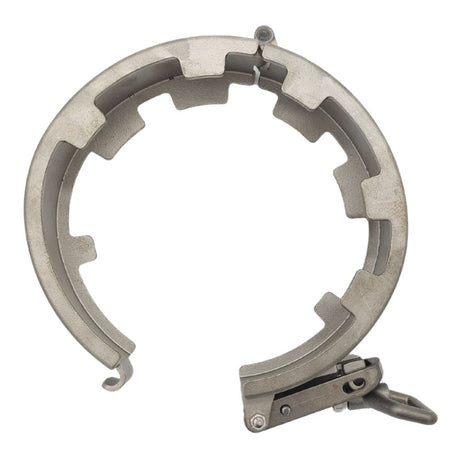
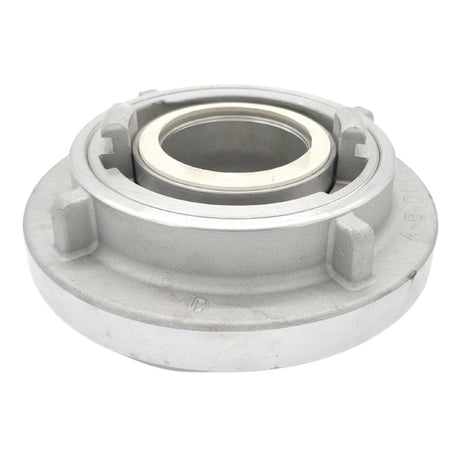
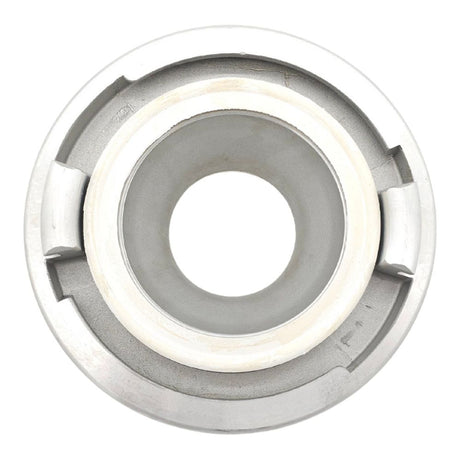
Unicone Coupling Serrated Tail (Stainless Steel)
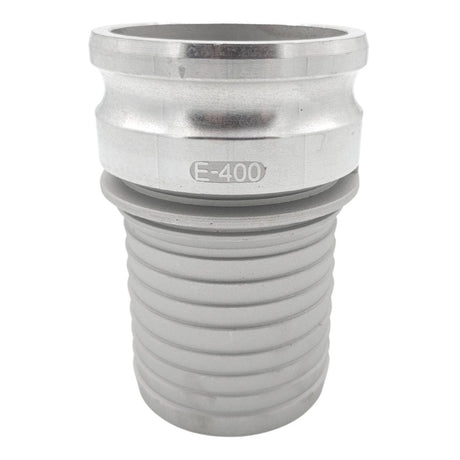
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableCamlock Coupling Part E Male Hose Tail (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Male Serrated Hose Tail (Gunmetal)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female Swivel (Stainless Steel)
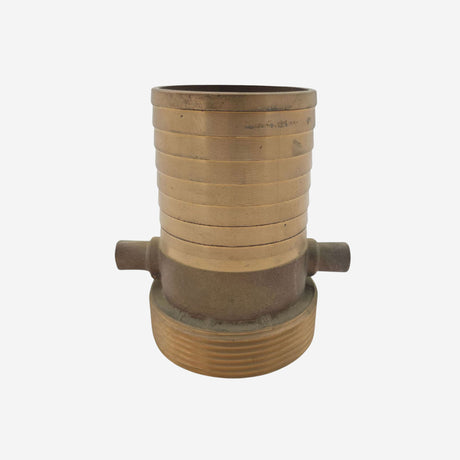
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableTank Wagon Coupling Male VK (Brass)
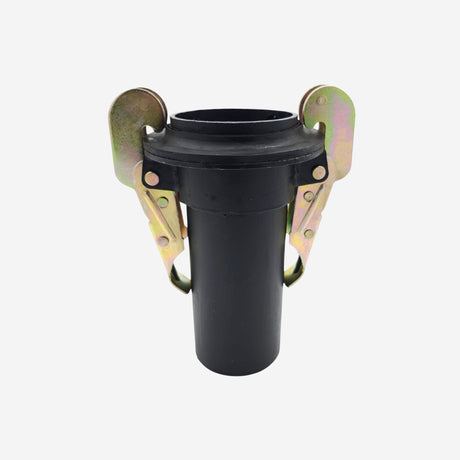
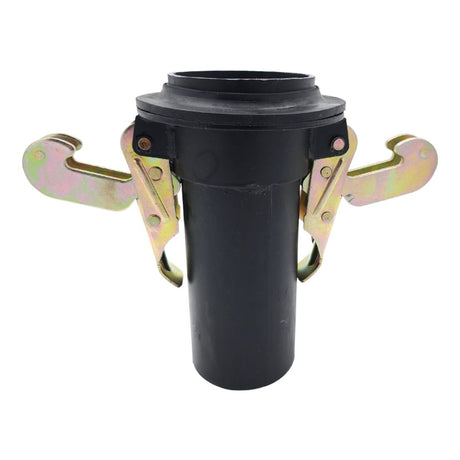
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableToggle Hose Coupling Male with Two Clamps
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Female Serrated Hose Tail (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
URT Male Weld Stub (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableCamlock Coupling Part D Female to BSP Female (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
URT Coupling Male to Female Reducer (Plastic)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableURT Coupling Male Smooth Hose Tail (Steel)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
URT Coupling Female to BSP Female (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableURT Coupling Female Reducing Hose Tail (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
URT Blank Cap (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
Camlock Coupling Replacement Arm (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableCamlock Coupling Male to BSP Female Reducer (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableCamlock Coupling Female to BSP Male Reducer (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableCamlock Coupling Female to BSP Female Reducer (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable- £0.01Unit price /Unavailable
Wilcox Coupling Male Weld Stub (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Male to BSP Female (Gunmetal)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Male Spool (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Female Swivel To BSP Male (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Female Swivel To BSP Female (Gunmetal)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableWilcox Coupling Female Serrated Hose Tail (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Male (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female Swivel Lockable (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female Swivel (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female Lockable (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling to BSP Female (Aluminium)
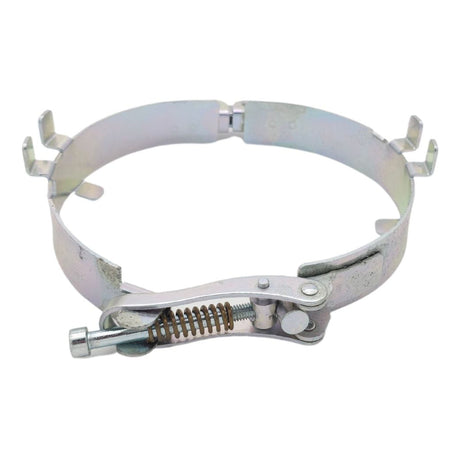
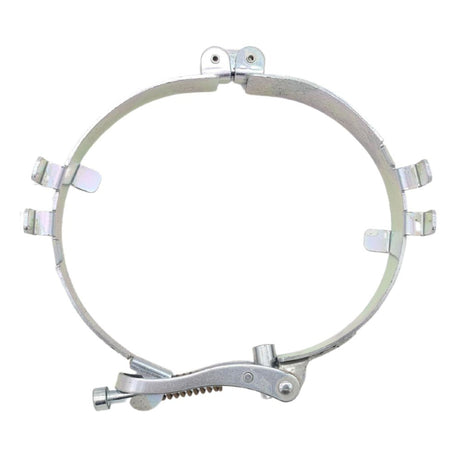
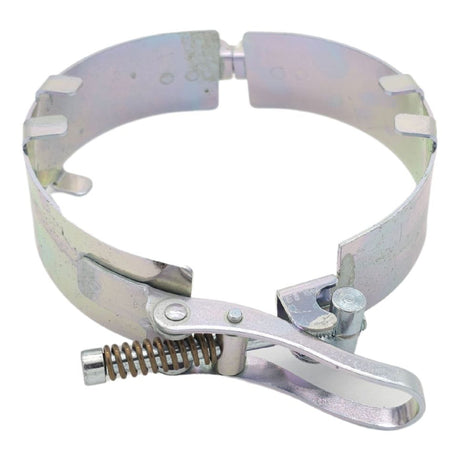
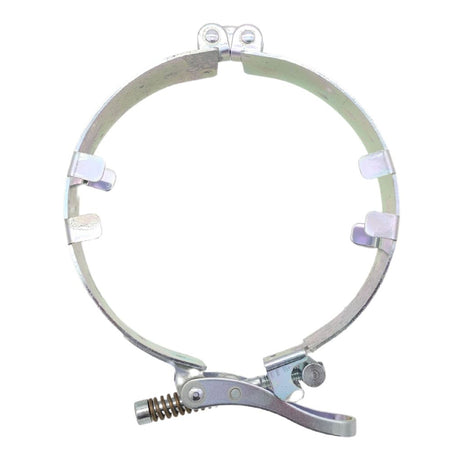
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Safety Strap 133 To 89 (Mild Steel)
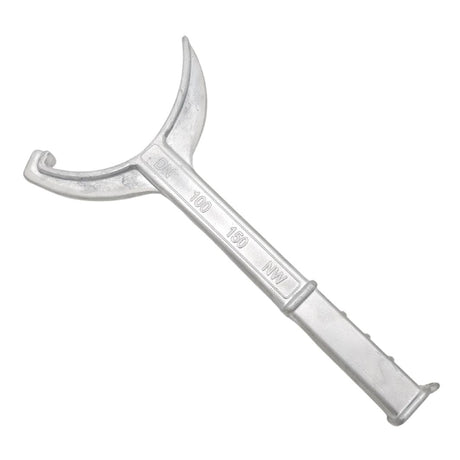
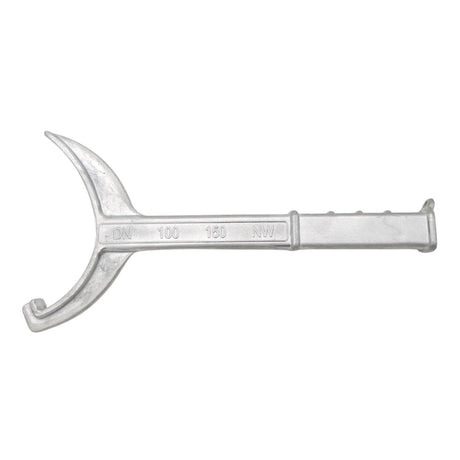
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Spanner 100mm-150mm
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Segmented Binding Tail Set (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Seal (White Rubber)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Seal (Silicone)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Seal (Green Viton)
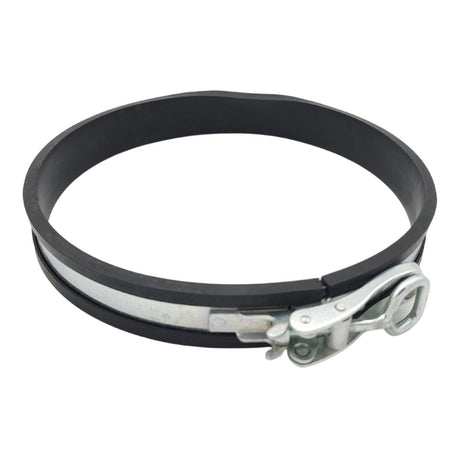
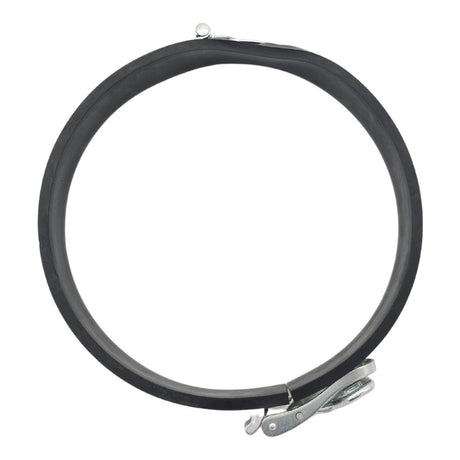
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Safety Strap (Rubber Lined)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Safety Strap (Stainless Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Safety Strap (Mild Steel)
£0.01Unit price /UnavailableStorz Coupling Reducer (Aluminium)
£0.01Unit price /Unavailable